Figure 1.
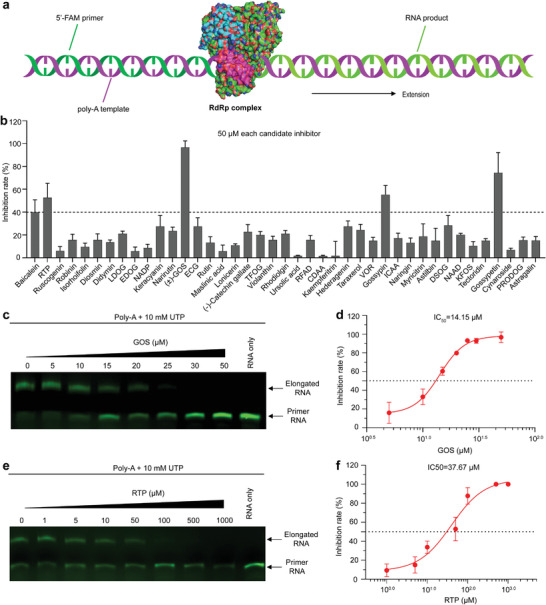
Inhibition of SARS‐CoV‐2 RdRp by GOS. a) Schematic diagram of the RNA extension assay based on SARS‐CoV‐2 RdRp. b) The screening of candidate RdRp inhibitor compounds from cotton plant using RNA extension assay based on SARS‐CoV‐2 RdRp. The working concentration of the inhibitors was 50 µm. LDOG: Luteolin‐7,3″‐di‐O‐glucoside; ECG: Epicatechin gallate; TFOG: Taxifolin‐3″‐O‐glucoside; RFAD: Riboflavin 5″‐Adenosine Diphosphate; CDAA: Cyclic di‐3″,5″‐adenylic acid; VOR: Vitexin‐2‐O‐rhamnoside; ICAA: Isochlorogenic acid A; DSOG: Diosmetin‐7‐O‐glucoside; NAAD: Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide; KFOS: Kaempferol‐3‐O‐sambubioside; PRODOG: Pinoresinol‐4,4″‐O‐di‐O‐glucoside. c,e) Gel‐based assays of the elongation of partial RNA duplexes by the purified SARS‐COV‐2 RdRp, and inhibition of this elongation by GOS (c) and RTP (e). d,f), Inhibition curves for GOS (d) and RTP (f) activity, calculated with data from the fluorescence‐based assays. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. (n = 3).
