Figure 1.
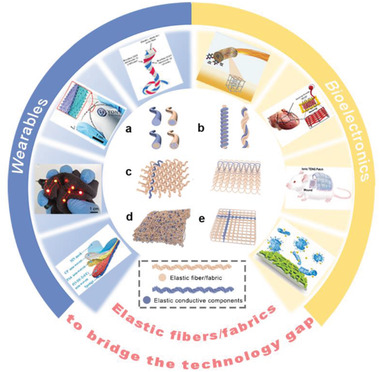
Schematic illustration of the structures of elastic materials in the form of fiber, yarn, fabric, and their integration strategies with electrodes. a) The typical cross‐section structures (core–shell, island structure, etc.) of elastic fibers or elastic conductive fibers. b) Coiling or twisting to realize elastic conductive yarns. c) Accurate incorporation of elastic conductive yarn interspersed in (left) woven and (right) knitted fabrics. d) Diverse incorporation of conductive elastic fibers in a nonwoven fabric via electrospinning, microfluidic spinning, or blowing spinning, etc. e) Accurate printing of elastic conductive ink in 3D elastic fabric.[ 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ] The surrounding elements are reproduced with permissions from references in the order of counterclockwise on the left half and clockwise on the right one. Reproduced with permission.[ 39 ] Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. Reproduced with permission.[ 40 ] Copyright 2019, Wiley‐VCH. Reproduced with permission.[ 41 ] Copyright 2020, Wiley‐VCH. Reproduced with permission.[ 42 ] Copyright 2021, Wiley‐VCH. Reproduced with permission.[ 43 ] Copyright 2016, Wiley‐VCH. Reproduced with permission.[ 44 ] Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. Reproduced with permission.[ 45 ] Copyright 2021, Elsevier. Reproduced with permission.[ 46 ] Copyright 2018, The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).
