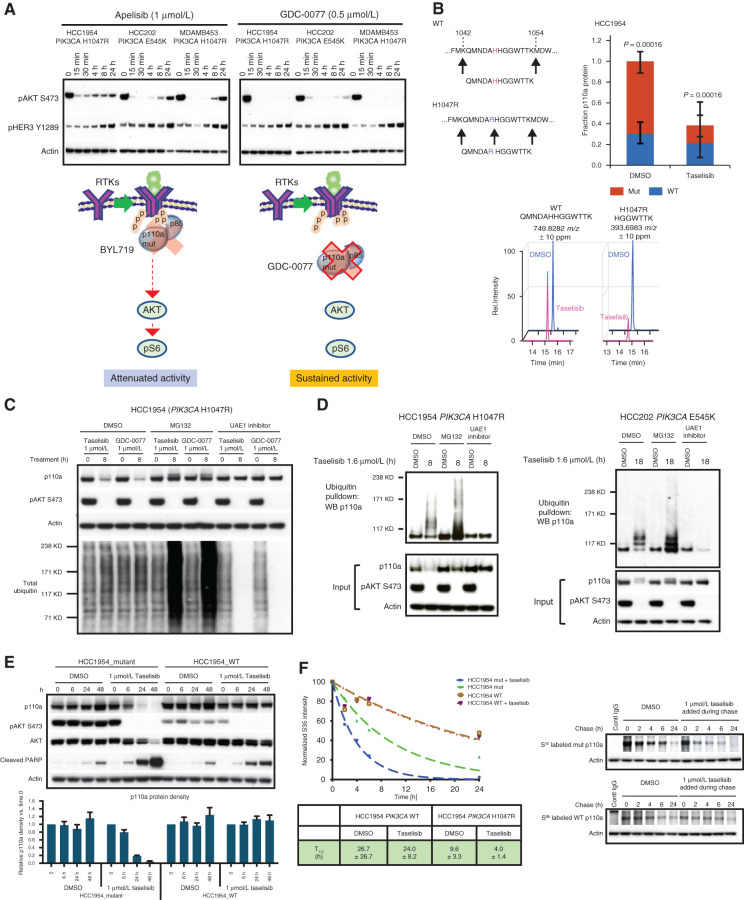
Figure 3.
Taselisib depletes mutant p110a protein through ubiquitin and proteasome mechanism in a dose- and time-dependent manner. A, Western blots of the inhibitor response in PI3K signaling (pHER3 and pAKT) in PIK3CA-mutant (HCC1954, HCC202, and MDA-MB-453) cell lines treated with 1 μmol/L BYL719 or 0.5 μmol/L GDC-0077 for indicated time points. B, Mass spectrometry of HCC1954 cells treated for 24 hours with 500 nmol/L taselisib. A neotryptic peptide generated from PIK3CA H1047R was used to assess mutant protein levels compared with WT protein in the same lysate. C, Rescue of taselisib- or GDC-0077–mediated p110a degradation in HCC1954 cells by either a proteasome inhibitor (MG132) or a ubiquitin activating enzyme E1 (UAE1) inhibitor. D, HCC1954 PIK3CA H1047R cells were treated 8 hours or HCC202 PIK3CA E545K cells were treated for 18 hours with either DMSO or 1 μmol/L taselisib ± MG132 or ± UAE1 inhibitor. Protein lysates were run on Western blot and probed with antibodies to p110a, pAKT, and β-actin, or ubiquitinated proteins were pulled down with TUBE1 reagent and then blotted with anti-p110a antibody. E, HCC1954 cells engineered to be isogenic for PIK3CA-mutant or PIK3CA-WT were treated with 1 μmol/L taselisib for up to 48 hours followed by Western blotting. Experimental replicates n = 3 were used to quantify p110a. F, Pulse-chase of isogenic cell lines, HCC1954_mutant and HCC1954_WT. PI3K inhibitor taselisib at 1 μmol/L was added during the chase. Pulldown with p110a antibody was followed by autoradiography and data fit to a single exponential decay function.