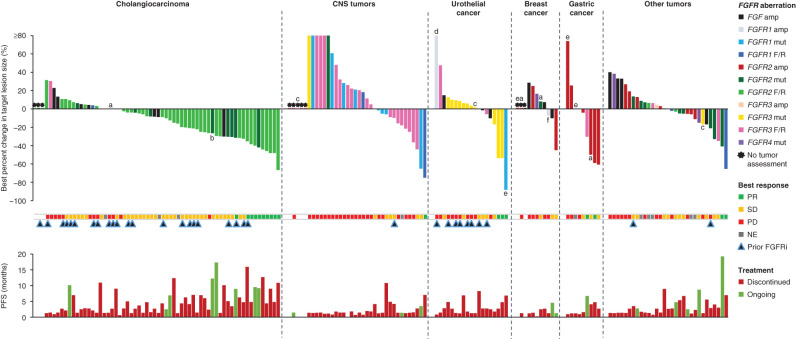
Figure 2.
Individual response and treatment outcome by tumor type in patients who received futibatinib 20 mg once daily. This figure shows individual treatment outcomes organized by tumor type, color coded for FGFR aberration in patients who received futibatinib 20 mg once daily (n = 170). RECIST v1.1 criteria were used for tumor response assessment for all tumor types except CNS tumors, for which RANO criteria were used to assess tumor response. Several patients (n = 14; indicated with a–f) had more than one type of FGF/FGFR aberration. In addition to the FGF/FGFR aberration indicated by the color-coded bars, patients had (a) FGFR2 F/R, (b) FGF3/4/19 amp, (c) FGFR3 F/R, (d) FGFR3 mut, (e) FGF3/19 amp, or (f) FGFR2/3 amp. amp, amplification; FGFRi, FGFR inhibitor; F/R, fusion/rearrangement; mut, point mutation; NE, not evaluable; PD, progressive disease.