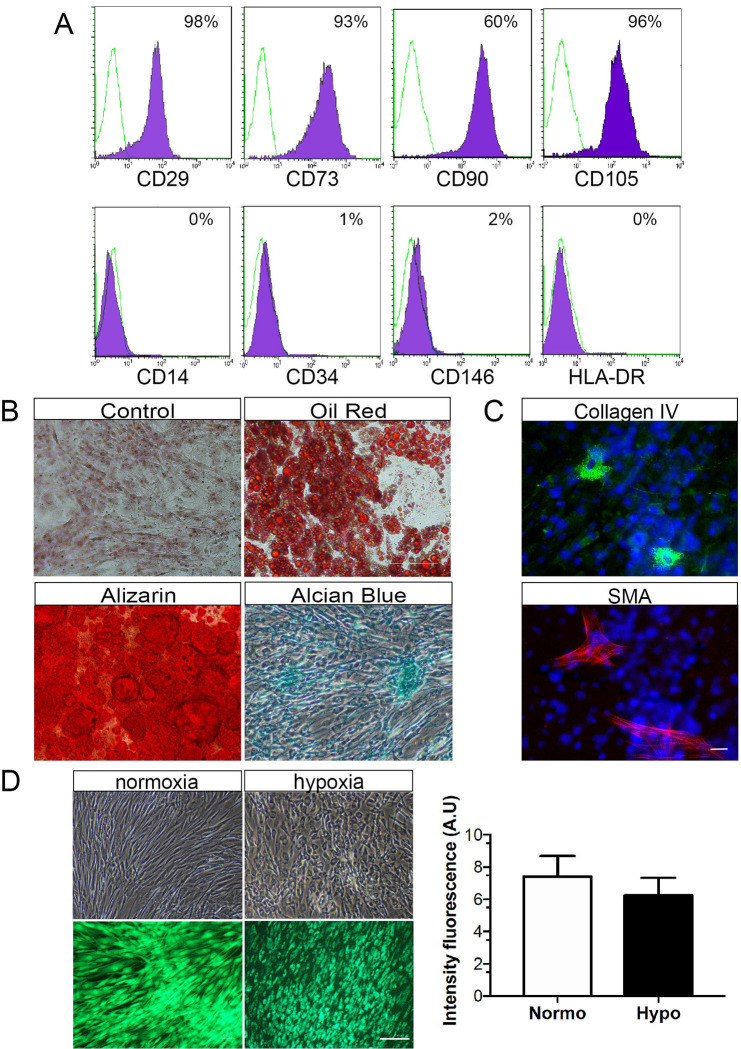
Fig 1. Characterization of hASCs.
(A) Flow cytometry histograms shows that hASC were positive for CD29, CD73, CD90 and CD105, while negative for CD14, CD34, CD146 and HDLA-DR. The percentage of cells staining for each marker (purple area) and the respective isotype-control (green line) are provided. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy imaging of hASCs exposed to adipogenic, osteogenic, or chondrogenic differentiation media. Accumulation of intracellular lipid vacuoles shown by oil red-O staining, calcium-rich extracellular matrix as evidenced by Alizarin red S, and glycosaminoglycans stained with Alcian Blue. (C) Immunocytochemistry detection shows α-SMA and collagen-IV-positive hASCs. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye (blue). (D) After normoxic and hypoxic preconditioning, hASC displayed spindle-shaped fibroblast-like morphology. Staining with Calcein-AM indicated that hASC viability remained unaffected by hypoxic preconditioning. Scale bars: 25μm in C and 75μm in D. Values are expressed as means ± SD of at least three independent experiments (n = 8).