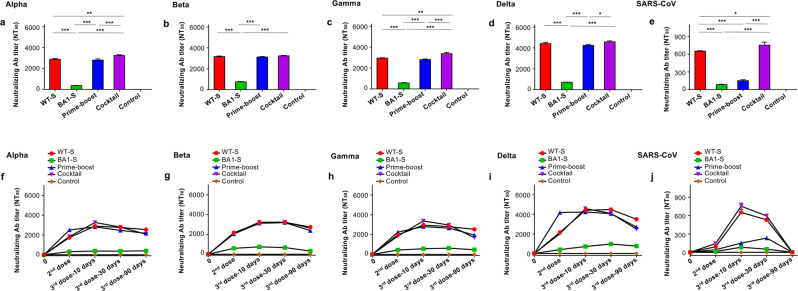
Fig. 3. Cocktail or prime-boost of SARS-CoV-2 WT-S and BA1-S proteins induced potent and durable neutralizing antibodies against other SARS-CoV-2 VOCs and SARS-CoV.
BALB/c mouse sera collected 10 days after the second immunization and, 10, 30, and 90 days, respectively, after the third immunization of WT-S, BA1-S, WT-S prime and BA1-S boost, WT-S and BA1-S cocktail, or PBS control were evaluated for neutralizing antibodies against pseudotyped viruses encoding S protein of SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant containing 10 amino acid mutations (69–70 deletions, 145 deletion, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, and D1118H) in the S protein, Beta/Gamma variants containing K417N/T, E484K, and N501Y mutations in the RBD, and Delta variant containing L452R, T478K, and P681R mutations in the S1 subunit, as well as the original SARS-CoV. NT50 was expressed as 50% neutralizing antibody titers against pseudovirus infection in hACE2/293T cells. NT50 against pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 Alpha (a), Beta (b), Gamma (c), Delta (d) variants, and SARS-CoV (e) 10 days after the third immunization, as well as against pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 Alpha (f), Beta (g), Gamma (h), Delta (i) variants, and SARS-CoV (j) 10 days after the second immunization and 10, 30, and 90 days, respectively, after the third immunization. The data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m of quadruple wells from pooled sera of five mice in each group. Statistical significance among different vaccination groups was analyzed using Ordinary one-way ANOVA, and * (P < 0.05), ** (P < 0.01), and *** (P < 0.001) indicate significant differences. The experiments were repeated twice, leading to similar results.