Figure 1.
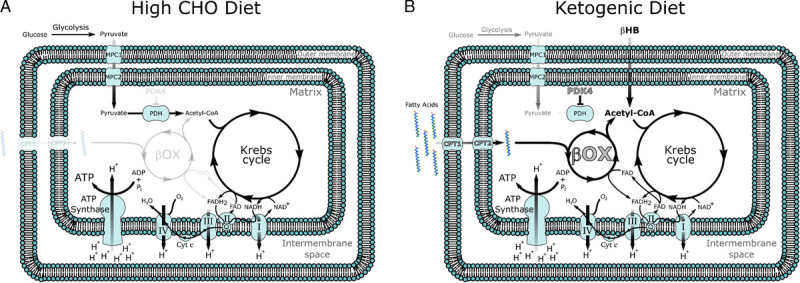
Mitochondrial metabolism on (A) a high-carbohydrate (CHO) versus (B) a ketogenic diet (KD). Note that on a high-CHO diet, acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) is primarily synthesized from pyruvate generated from the breakdown of glucose in the cytoplasm. By contrast, on a ketogenic diet, βHB can directly enter the mitochondria and be converted into acetyl-CoA. The increased oxidation of fatty acids also activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) transcription factors resulting in the upregulation (in gray with black outline) of key PPAR target genes such as fatty acid transporters (carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 and 2), enzymes of β-oxidation, as well as PDK 4, driving fatty acid oxidation and inhibiting CHO oxidation, respectively.
