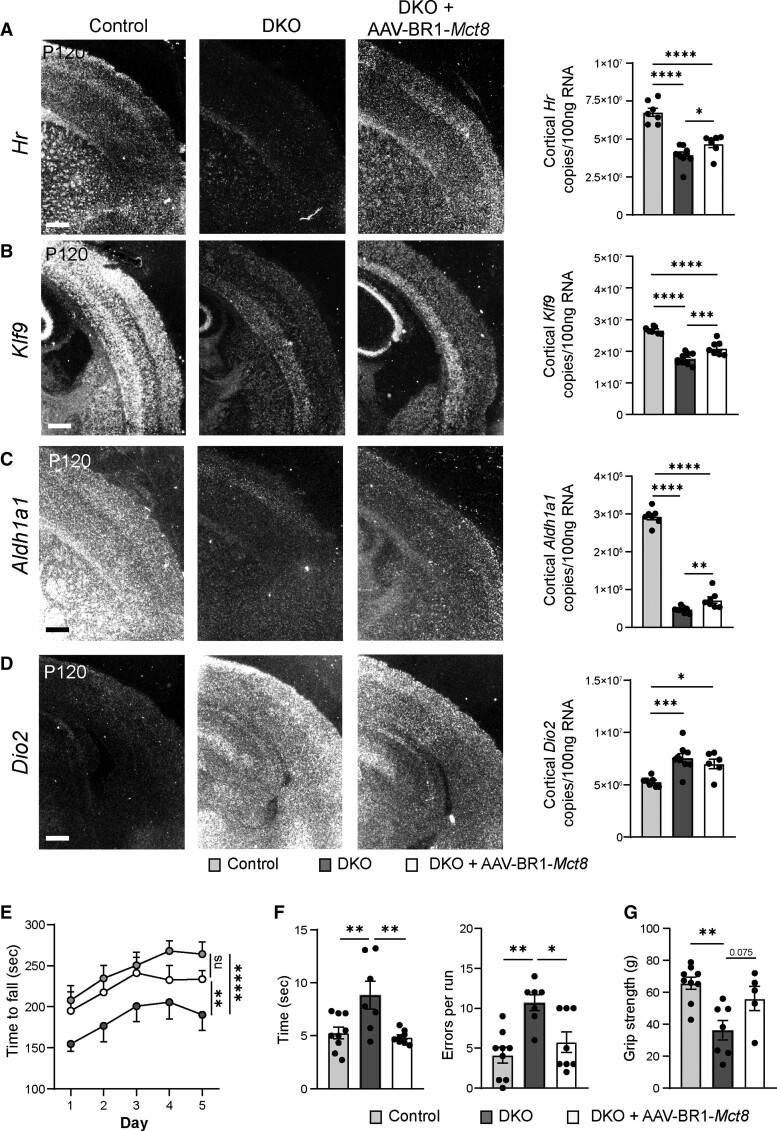
Figure 4.
AAV-BR1-Mct8 treatment improves expression of TH-dependent genes and motor function in DKO mice. (A and B) AAV-BR1-Mct8 injected at P0 increased the expression of neuronal Hr and Klf9 in the cortex of DKO mice at P120. Gene expression was visualized by in situ hybridization and quantified by qPCR. In situ hybridization images are representative for several replicates (Supplementary Table 1). Scale bar = 100 µm. One-way ANOVA: Hr, F(2/20) = 36.92, P < 0.0001; Klf9, F(2/20) = 52.79, P < 0.0001; Holm–Sidak’s post hoc test. (C and D) AAV-BR1-Mct8 injected at P0 increased the expression of astrocytic Aldh1a1 (C) in the cortex of DKO mice at P120. The elevated cortical Dio2 expression (D) in DKO mice was not reduced by AAV-BR1-Mct8. Scale bar = 100 µm. One-way ANOVA: Aldh1a1, F(2/20) = 440.4, P < 0.0001; Dio2, F(2/19) = 10.01, P = 0.0011; Holm–Sidak’s post hoc test. (E) AAV-BR1-Mct8 treatment at P0 prolonged the time DKO mice were able to balance on the rotarod as a sign of improved coordination and motor learning. Mice were assessed on five consecutive days starting at P120. Repeated-measures ANOVA, F(2/26) = 5.045, P = 0.0141; Holm–Sidak’s post hoc test. (F) AAV-BR1-Mct8 treatment reduced the time DKO mice needed to cross the beam and led to a trend towards fewer errors, indicating better motor coordination. One-way ANOVA: time, F(2/21) = 7.567, P = 0.0034; errors, F(2/21) = 9.274, P = 0.0013; Holm–Sidak’s post hoc test. (G) AAV-BR1-Mct8 treatment tended to increase the grip strength of DKO mice in comparison to control animals. One-way ANOVA, F(2/18) = 8.301, P = 0.0028; Holm–Sidak’s post hoc test. Each dot represents one animal. Means ± SEM are shown. ns = non-significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.