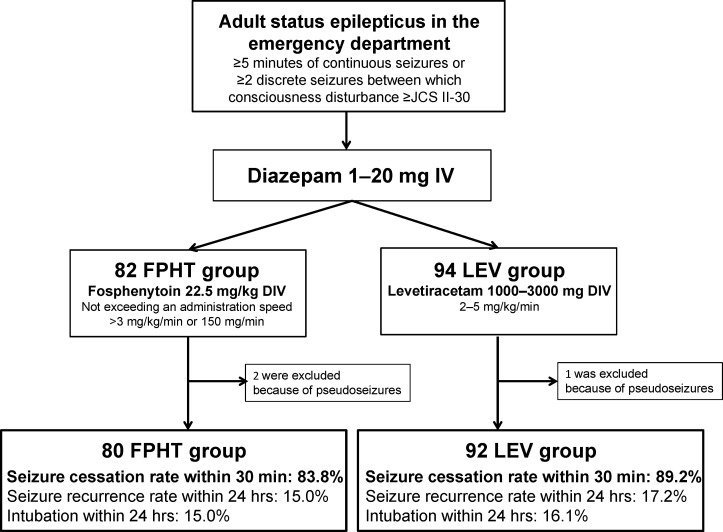
Figure 1.
Study outline and outcomes. The study protocol was immediately performed on patients with status epilepticus who met the eligibility criteria in the emergency department. Registration was simultaneously conducted with the administration of diazepam and patients were randomised to the FPHT or LEV group. In both groups, diazepam was intravenously administered at 1–20 mg. In the 82 patients in the FPHT group, FPHT was intravenously administered at 22.5 mg/kg after diazepam at an administration rate not exceeding 3 mg/kg/min or 150 mg/min. In the 94 patients in the LEV group, LEV was intravenously administered at 1000–3000 mg after diazepam at an administration rate of 2–5 mg/kg/min. Two patients in the FPHT group and one in the LEV group were excluded because they were diagnosed with pseudoseizures. Seizure cessation rates within 30 min were 83.8% in the FPHT group and 89.2% in the LEV group. DIV, drip intravenous injection;FPHT, fosphenytoin; IV, intravenously; LEV, levetiracetam;JCS, Japan Coma Scale.