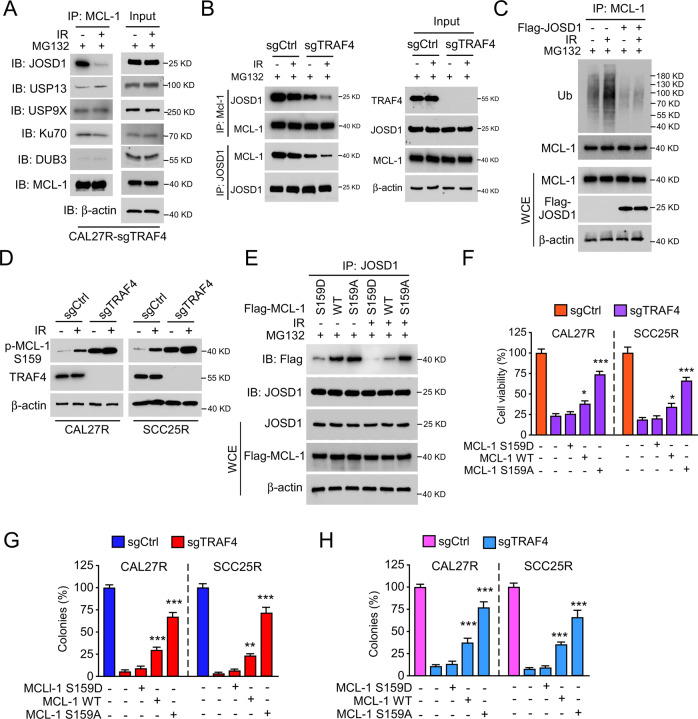
Fig. 5. Irradiation disrupts the interaction between JOSD1 and MCL-1.
A TRAF4 knockout CAL27R cells were treated with/without IR (2 Gy) for 20 min, and WCE was subjected to co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analysis. B Immunoblotting for IP-mediated MCL-1 and JOSD1 expression in TRAF4 knockout CAL27R cells treated with/without IR (2 Gy) for 20 min. C CAL27R cells were transfected with Flag-JOSD1 for 48 h, followed by IR (2 Gy) treated for 20 min. IP assay was performed to detect MCL-1 ubiquitination. D Immunoblotting for p-MCL-1 S159 expression in TRAF4 knockout CAL27R and SCC25R cells treated with/without IR (2 Gy) for 72 h. E CAL27R cells were transfected with Flag-MCL1 WT, Flag-MCL1 S159D and Flag-MCL1 S159A for 48 h, followed by IR (2 Gy) treated for 20 min. WCE was subjected to co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analysis. F–H Transfected with Flag-MCL1 S159A mutant restored proliferation of TRAF4 knockout OSCC cells. TRAF4 knockout CAL27R and SCC25R cells were transfected with Flag-MCL1 WT, Flag-MCL1 S159D and Flag-MCL1 S159A for 48 h. MTS assay was used to determine the cell viability (F), plate colony formation assay to analyze the colony formation (G) and soft agar assay to assess the anchorage-independent cell growth (H). All data are means ± s.e.m. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, a significant difference between groups as indicated.