FIGURE 1.
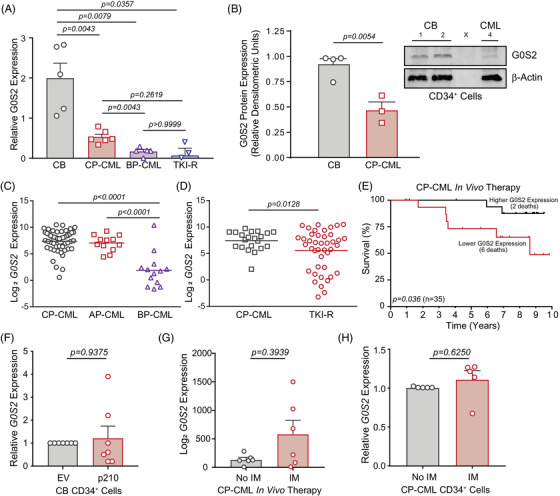
G0/G1 switch gene 2 (G0S2) is downregulated in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) disease progression and imatinib resistance in a BCR::ABL1 kinase‐independent manner. (A) Bar graph shows G0S2 mRNA levels as quantified by reverse transcription‐quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT‐qPCR) on primary CD34+ cells from human cord blood (CB) (n = 5), chronic phase CML (CP‐CML) (n = 6), blast phase CML (BP‐CML) (n = 5) and tyrosine kinase inhibitor‐resistant (TKI‐R) patients harbouring native BCR::ABL1 (n = 3). (B) G0S2 protein levels were analysed by immunoblot on primary CD34+ cells from human CB (n = 4) versus CP‐CML patients (n = 3). β‐Actin was analysed as a loading control. Bar graph represents relative densitometric units for primary cell immunoblot data. (C and D) Dot plots from RNAseq data demonstrate reduced G0S2 mRNA levels in mononuclear cells from BP‐CML (n = 13) compared with CP‐CML (n = 53) and accelerated phase CML (AP‐CML) (n = 12) patients (C), and in TKI‐resistant (n = 42) compared with newly diagnosed (n = 21) CP‐CML patients (D). (E) Kaplan–Meier curve shows relative overall survival (OS) of newly diagnosed CP‐CML patients (n = 35) with G0S2 mRNA expression in CD34+ cells (prior to imatinib therapy) above (high, n = 18) or below (low, n = 17) the value at a bimodal separation. (F) Bar graph shows relative G0S2 mRNA levels in CB CD34+ cells engineered for p210 BCR::ABL1 ectopic expression (n = 7) versus the empty vector (EV) control (n = 7). (G) Bar graph demonstrates published microarray data showing G0S2 mRNA expression levels in CP‐CML CD34+ cells before and after in vivo imatinib (IM) therapy (400 mg daily) for 7 days (n = 6) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geoprofiles, GDS3518, 213524_s_at, p = .3939). 39 (H) Bar graph shows G0S2 mRNA expression in primary CP‐CML CD34+ cells (n = 5) cultured ex vivo ± IM (1 µM, 24 h) as assessed by RT‐qPCR. GUS mRNA levels were used as a loading control. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).
