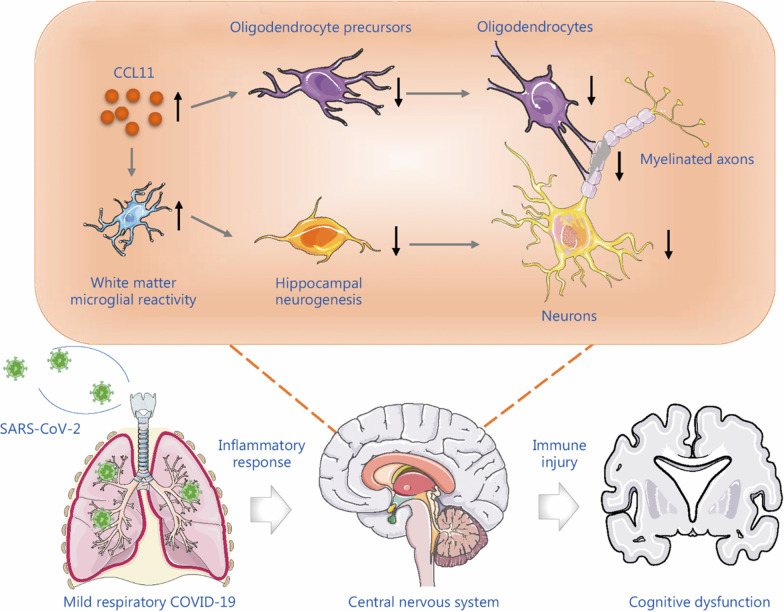
Fig. 1.
Neuroinflammation is the central pathophysiology that links mild respiratory COVID-19 to cognitive impairment. Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause an excessive peripheral inflammatory response to result in the consequent immune injury in CNS. The elevated CSF CCL11 and white matter microglial reactivity are associated with multi-lineage cellular dysregulation in the CNS, including impaired hippocampal neurogenesis, persistent loss of oligodendrocytes, and myelinated axons. SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, CCL11 C-C motif chemokine ligand 11, CNS central nervous system, CSF cerebrospinal fluid