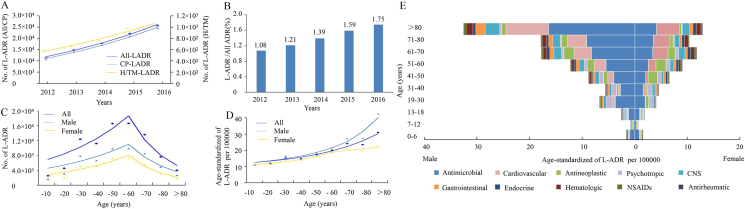
Figure 1.
The overall trend and epidemiological characteristics of L-ADR reports in Mainland China. (A) Temporal changes of L-ADR reports by implicated agent classes. The fitting models for All-LADR, CP-LADR and H/TM-LADR were regressed with APC values as 17.54, 17.75 and 12.74, respectively. (B) Proportion of L-ADR reports in all types of ADRs over the year. (C) Distribution trends of L-ADR reports in different sex and age groups showed two-phase pattern with increasing trend below 60 years old and decreasing trend beyond 60 years old. APC values for all sex are 22.89 (< 60 years) and −35.55 (> 60 years); for male ones are 20.81 (< 60 years) and −33.05 (> 60 years); and for female ones are 25.79 (< 60 years) and −39.31 (> 60 years), respectively. (D) Distribution trends of L-ADR reports in different sex and age groups after adjustment by the national age distribution showed increasing patterns. APC values for all sex is 27.50; for male ones are 31.55 (< 70 years) and 39.38 (> 70 years); for female ones are 40.31 (< 60 years) and 9.87 (> 60 years). (E) Proportions of implicated CP drug subclasses in different sex and age groups according to the age-distribution adjusted reporting numbers. X-axis indicates the proportion of L-ADR in general population (per 100,000) and Y-axis indicates age groups.