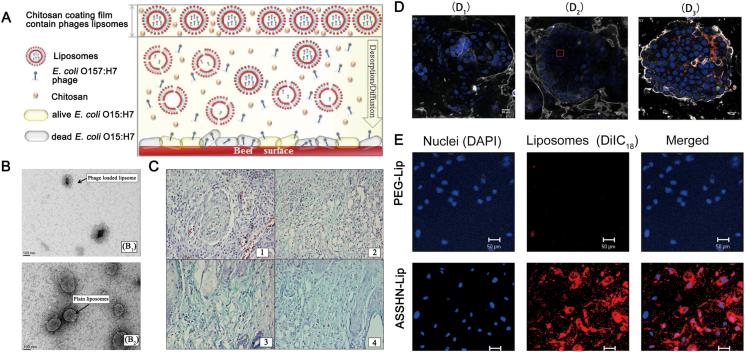
Figure 2.
(A) Liposome-encapsulated phage with chitosan film against E. coli in beef. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 41. Copyright © 2017, Elsevier Ltd (B) Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) images of liposomes. Phage loaded liposomes (B1) and plain liposomes (B2). Reprinted with permission from Ref. 89. Copyright © 2018 by the authors (C) Collagen formation and treatment in wound tissue of mice on day 5 post-infection indicated by Masson's Trichrome staining (C1): Diabetic untreated mice (infected control mice) displayed infiltration of neutrophils along with fibroblastic condensation (C2): Free cocktail of phages (FCP)-treated mice indicated intermediate stage of presence of mature collagen fibrils along with collagen formation (C3): Liposome cocktail of phages (LCP)-treated mice showed the reduction of inflammatory cells and thin fibrils of mature collagen present with decreased vascularity (C4): Clarithromycin-treated mice displayed the presence of mature collagen fibers along with negligible inflammation, indicating wound healing. Reprinted with permission from Ref. Copyright © 2018 by the authors (D) The confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) images of the cells (D1), phages (D2), and PPE (D3). Reprinted with permission from Ref. 40. Copyright © 2019 by the authors (E) The CLSM images depicting the association of ASSHN-Lip with hEPCs. Red and Blue fluorescence display the liposomes and nuclei respectively. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 44. Copyright © 2017, Elsevier Ltd.