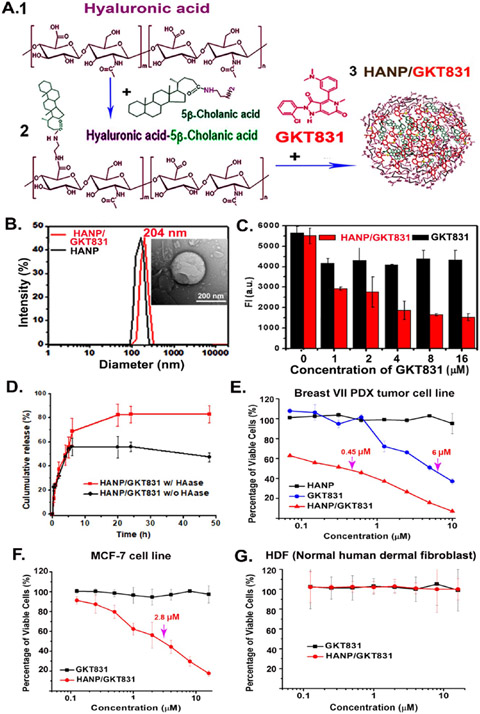
Figure 2.
Production and characterization of HANP/GKT831. (A) 200 kDa HA (1) was conjugated with 5β-cholanic acid to form HA-CA (2). GKT831 was encapsulated into HA-CA by self-assembling, resulting in HANP/GKT831 (3). (B) Hydrodynamic size of HANP (180 nm) and HANP/GKT831 (204 nm). (inset) TEM image of a HANP/GKT831. (C) Quantification of the level of intracellular ROS by DCFDA assay. Breast cancer MCF-7 cells treated with various concentrations of HANP/GKT831 or GKT831. DCFDA assay was performed 24 h following treatment. Fluorescence intensity (FI, a.u.) of treated cells represents the level of ROS, mostly H2O2. The mean fluorescence intensity of four repeat samples is shown. (D) GKT831 release profile from HANP/GKT831 in the absence and presence of hyaluronidase (HAase). (E, F) SRB cell proliferation assay. IC50 of HANP/GKT831: Breast VII PDX-derived cell line (IC50 = 0.45 μM), MCF-7 cell line (IC50 = 2 μM). IC50 of GKT831: Breast VII PDX tumor cell line (6 μM) and MCF-7 cell line (>16 μM, not reached). Neither HANP/GKT831 nor GKT831 inhibited proliferation of normal HDF (G).