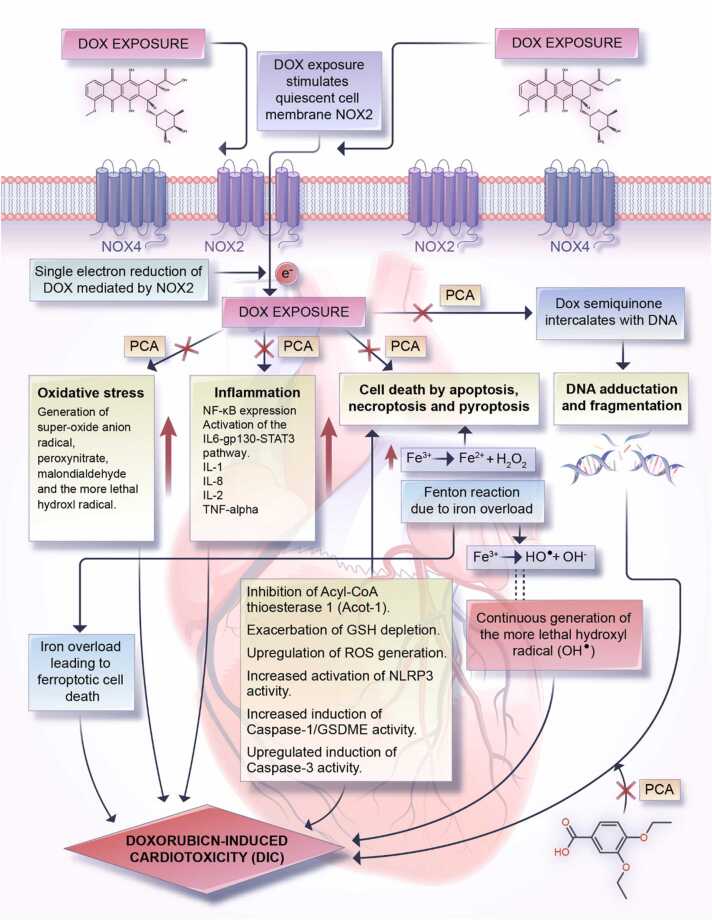
Fig. 3.
Summarization of DIC mechanisms and potential ameliorative role for PCA. Generation of DOX-semiquinone via an NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2)-catalyzed single electron reduction is the common point for the induction of molecular toxicities such as oxidative stress, inflammation, DNA fragmentation/adduction, and cell deaths of several forms (apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis) in cardiomyocytes. Left unchecked or unregulated, these processes collectively result in DIC. Interestingly, PCA, due to its established antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cell death, and DNA-protecting activities abrogates the induction of molecular toxicities due to DOX-quinone generation thereby rescuing cardiac cells from DOX-induced injuries.