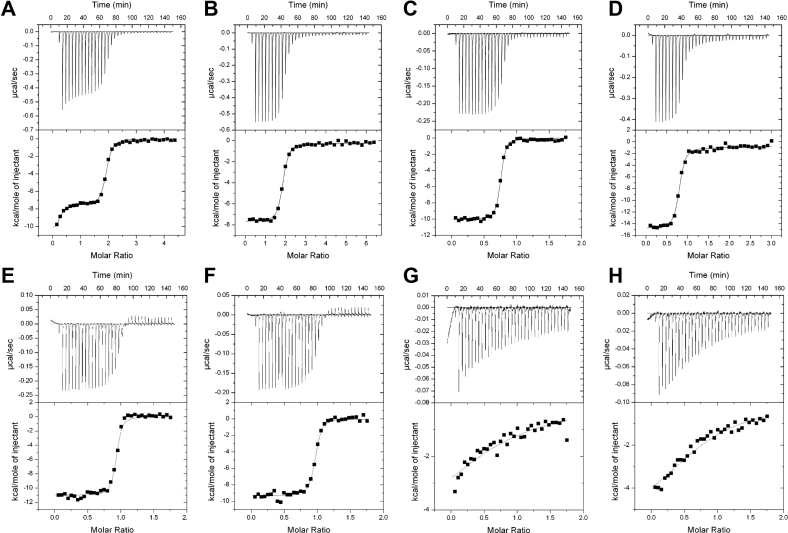
Figure 3.
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) binding assays. A and B, ITC measurement of Ca2+ binding to CaM12’-IQ at 27 °C (A) and 37 °C (B). The Ca2+ binding isotherms at 27 °C and 37 °C were fit to a two-site and one-site model, respectively. The apparent Ca2+ affinity () and enthalpy difference (ΔH1 and ΔH2) are given in Table 1. The CaM12’–IQ complex in the sample cell (10 μM at 27 °C or 8.0 μM at 37 °C, 1.5 ml) was titrated with aqueous CaCl2 (0.23 mM at 27 °C or 0.30 mM at 37 °C) using 35 injections of 10 μl each. C–D, ITC measurement of Ca2/CaM12’ binding to IQ at 27 °C (C) and 37 °C (D). The dissociation constant (KD) and enthalpy difference (ΔH) for Ca2/CaM12’ binding to IQ mutants (IQWT, IQY1649A, IQI1654A, IQY1657D, IQF1658D, and IQF1658A) are given in Table 3. The binding of Ca2/CaM12’ to IQK1662E could not be accurately measured by ITC because IQK1662E formed aggregated species under the conditions required for ITC. E–H, ITC measurement at 27 °C of Ca2/CaM12’ binding to IQF1649A (E), IQI1654A (F), IQY1657D (G), and IQF1658D (H). The IQ peptide concentrations for WT, Y1649A, and I1654A were each 10 μM (27 °C) or 7.0 μM (37 °C) in 1.5 ml in the sample cell for titration with 0.1 mM Ca2/CaM12’, and Y1657D and F1658D concentrations were each 50 μM in 1.5 ml for titration with 0.5 mM Ca2/CaM12’ using 35 injections of 10 μl each. CaM, calmodulin.