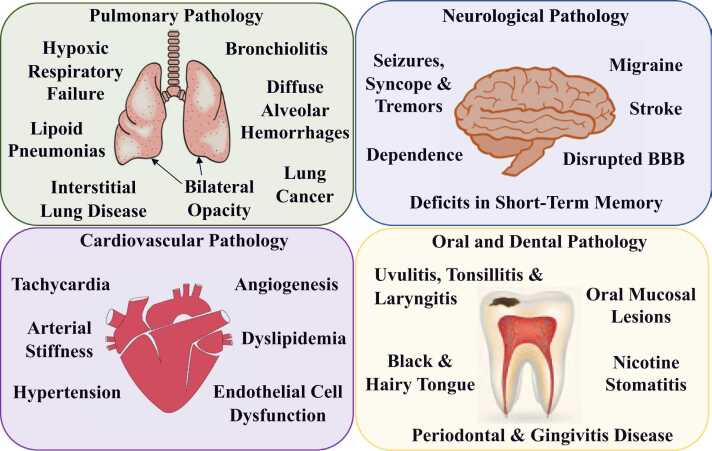
Fig. 2.
Summary of the clinical manifestations related to e-cigarette use. In the lungs vaping causes hypoxic respiratory failure, bilateral opacity, lipoid pneumonias, interstitial lung disease, bronchiolitis and diffuse alveolar hemorrhages [45]. Furthermore, increased production of CYP that metabolically activate PAHs from the e-vapor, has been linked to lung cancer by promoting ROS production and enhancing genotoxicity [25]. Vaping causes neurological disorders like seizures, syncope and tremors, disrupts the integrity of the BBB in the brain and increases the risk of developing a stroke [27], [28], [29], [93], [94], [95]. E-vapor could also induce changes in the embryonic brain that may contribute to future cognitive and behavioral abnormalities, like deficits in short-term memory [98]. Many e-cigarette brands contain acidified nicotine salts which result in delivery of high nicotine levels and potentially create dependence [7]. Impact of vaping on the cardiovascular system includes transient elevation of blood pressure, arterial stiffness, tachycardia, angiogenesis and dyslipidemia [30], [106], [107], [108], [112], [113], [114]. Additionally, vascular endothelial cells exposed to e-liquid showed decreased viability and higher production of ROS, leading to overall dysfunction [31]. Vaping also has detrimental effects in the oral cavity including black and hairy tongue, oral mucosal lesions, nicotine stomatitis, uvulitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, periodontal and gingivitis disease [29], [30], [31], [32], [33], [124], [125], [126], [127], [130], [131], [132], [133], [134].