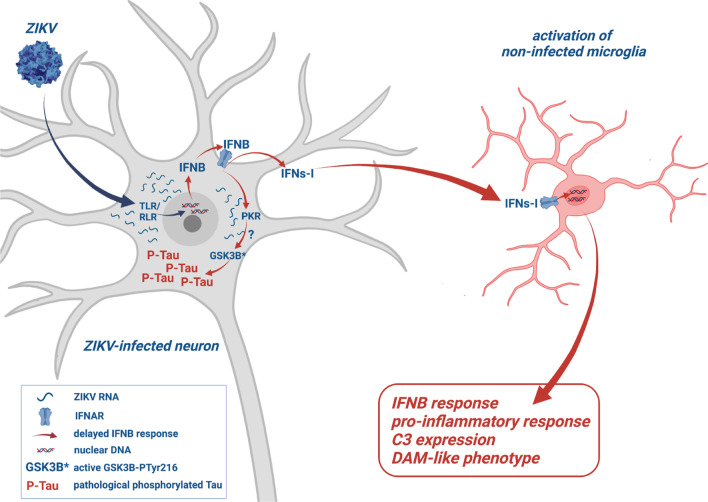
Fig. 9.
ZIKV-infection of neurons signals for IFNB-dependent microglia activation while inducing Tau phosphorylation. ZIKV-infected mature neurons from immunocompetent mice display a delayed IFNB response unable to stop viral replication leading to the accumulation of viral RNA in association with the induction of pathological phosphorylated Tau protein (P-Tau). ZIKV-infection leads to the activation of the expression of the gene coding for the RNA-dependent kinase PKR in PCNs and mouse brain. A role for PKR in the enhancement of P-Tau is proposed in relation with the capacity of PKR to be activated by viral cytoplasmic RNA and in turn activate GSK3B, one of the main kinases responsible of pTau. Following ZIKV infection of neurons, neuronal IFNs-I directly signal microglia for activation and the establishment of a DAM-like phenotype. The diagram was created using BioRender.com