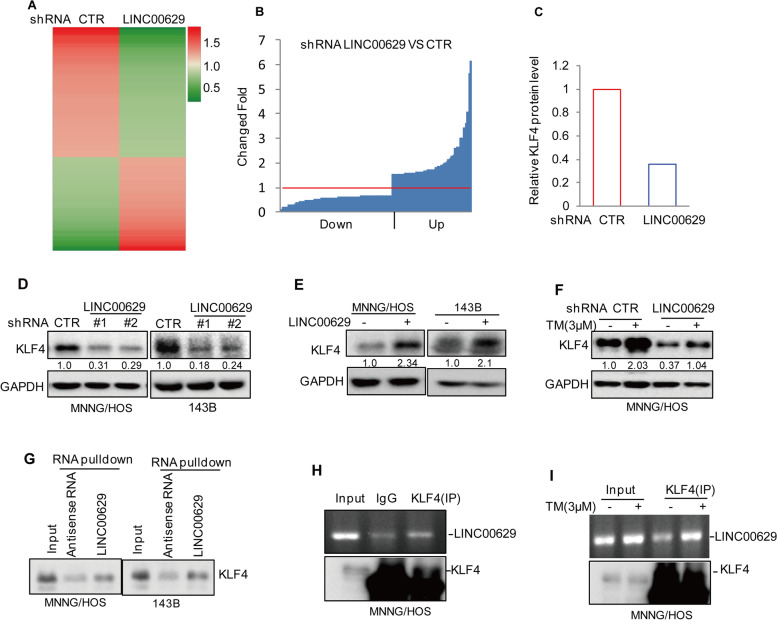
Fig. 3.
LINC00629 interacts with KLF4 and enhances KLF4 expression in osteosarcoma. A The differentially expressed proteins in MNNG/HOS cells with or without LINC00629 knockdown were identified by label-free quantitative proteomics. B The sixty-four downregulated and forty-six upregulated proteins are listed. C The fold change in KLF4 is listed. D The expression levels of KLF4 were detected by Western blot in MNNG/HOS and 143B cells with or without LINC00629 knockdown. Numbers represent the relative intensities of western blot bands of KLF4 to GAPDH. E The expression levels of KLF4 were detected by Western blot in MNNG/HOS and 143B cells with or without LINC00629 overexpression. Numbers represent the relative intensities of western blot bands of KLF4 to GAPDH. F MNNG/HOS cells with or without LINC00629 knockdown were treated with 3 μM TM for 36 h. The expression levels of KLF4 were detected by Western blot. Numbers represent the relative intensities of western blot bands of KLF4 to GAPDH. G Biotin-labelled LINC00629 or antisense RNA was pulled down with KLF4 in whole-cell lysates of MNNG/HOS and 143B cells. KLF4 protein was detected by Western blot. H KLF4 antibody (2 μg) was used to coprecipitate with LINC00629 in whole-cell lysates of MNNG/HOS cells. The levels of LINC00629 were detected by RT–PCR, and KLF4 protein levels were analysed by Western blot using a KLF4 antibody. I KLF4 antibody was used to coprecipitate with LINC00629 in whole-cell lysates of MNNG/HOS cells with or without 3 μM TM treatment. The levels of LINC00629 were detected by RT–PCR, and KLF4 protein levels were analysed by Western blot using a KLF4 antibody