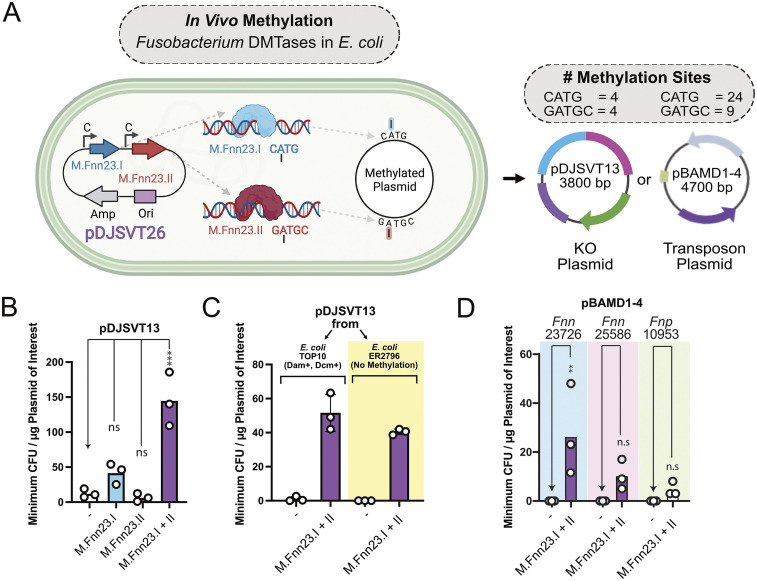
FIG 3.
In vivo methylation in E. coli expressing M.Fnn23.I and M.Fnn23.II enhanced plasmid transformation and chromosomal incorporation of plasmids and transposons. (A) Schematic of in vivo methylation of plasmids with F. nucleatum subsp. nucleatum 23726 MTases. The C above the arrow indicates a promoter that is constitutively active for constitutive expression in E. coli. (B) Transformation of pDJSVT13 was significantly increased by coexpressing M.Fnn23.I and M.Fnn23.II. (C) Comparison of methylation-positive (TOP10) and methylation-negative (ER2796) E. coli strains revealed that native E. coli methylation did not inhibit the transformation of pDJSVT13 when F. nucleatum subsp. nucleatum 23726 MTases were concurrently expressed. (D) In vivo methylation of the pBAMD1-4 transposon plasmid allowed for transformation and chromosomal transposon insertion into multiple strains of F. nucleatum. Statistical values are as follows: ns, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. For panel B data we used a two-way ANOVA; for panel D data we used Student's t test analysis.