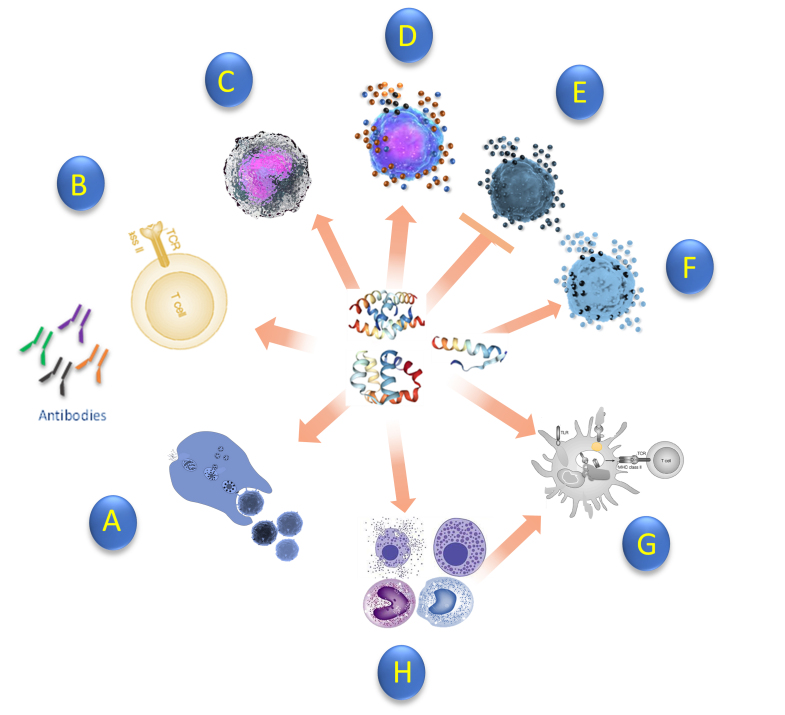
Figure 2.
Immunological response of antimicrobial peptide against bacteria. (A) Enhance phagocytosis (B) Naïve T cell (C) Induce chemokines (D) Induce pro-inflammatory cytokines (E) Suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines (F) Induce anti-inflammatory cytokines (G) Promote dendritic cell differentiation (H) Recruitment of monocytes, mast cells, and Macrophages which promotes cell differentiation. AMP exhibits antibacterial and immunomodulatory activities against pathogens. Peptides can also enhance bacterial phagocytosis of IgG-opsonized bacteria and suppress neutrophil apoptosis [163,164].