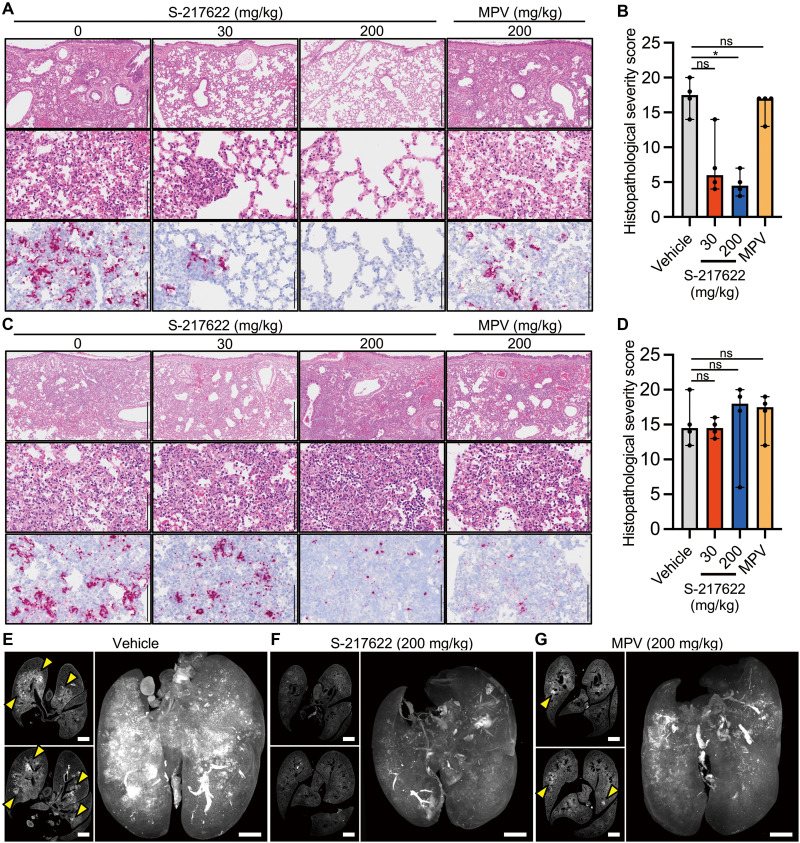
Fig. 5. Histopathological analysis of the lungs isolated from SARS-CoV-2-infected, antiviral-treated hamsters.
Hamsters were infected with 5,000 pfu of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant and euthanized at 4 dpi for histopathological examination. S-217622 (30 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg), molnupiravir (200 mg/kg), or vehicle control was administered from 0 to 3 dpi in the prophylactic setting (A and B) or 1 to 3 dpi in the therapeutic setting (C to G) twice a day following the schedules shown in Fig. 2B and Fig. 3A, respectively. (A and C) Representative histopathological images are shown for lung sections obtained from the animals treated with the indicated antivirals (n = 4 for each group). Upper and middle panels, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Lower panels, ISH targeting the n gene of SARS-CoV-2. Scale bars in upper panels, 500 μm. Scale bars in middle and lower panels, 100 μm. (B and D) Histopathological severity score of pneumonia was calculated based on the percentage of alveolitis area in a given section. Data are shown as the median score ± 95% confidential interval with each dot representing the score of each animal (n = 4). ns, not significant; *p < 0.05 by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s test. (E to G) Shown are cross-sectional images of lungs and 3D image reconstruction of whole lungs isolated from hamsters at 4 dpi. Infected hamsters were treated with vehicle (E), S-217622 (F), or MPV (G). The whole lung tissues were stained with anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibody and scanned by light sheet microscopy. Arrowheads indicate foci of SARS-CoV-2-positive alveoli. Scale bars, 2 mm.