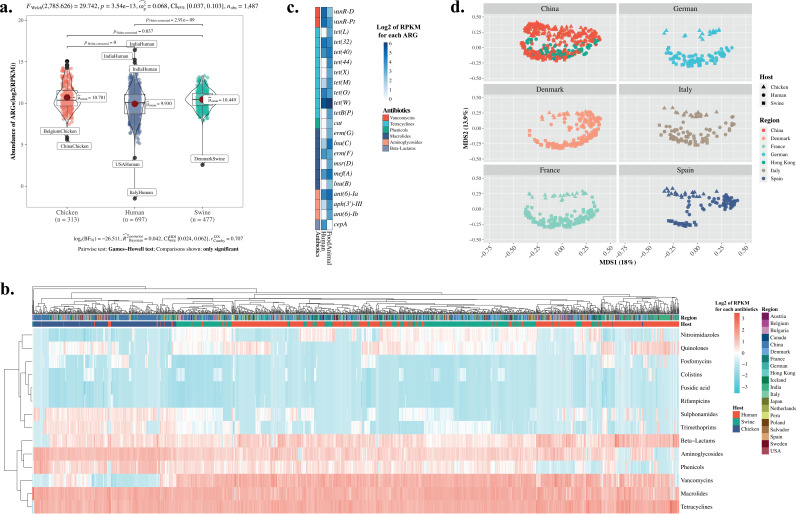
FIG 2.
Comparison for the relative abundance of acquired ARGs in human and food animals. (a) Relative abundance of summed ARGs in two types of human and food animal hosts, and each colored point represents one sample. The difference between two types of groups was compared using Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a P value of <0.05. (b) Heatmaps of the relative abundance of acquired ARGs in human and food animal fecal samples in the present study clustered in each group of hosts in columns and class of ARGs in rows. Relative abundance of each ARG has been standardized with base 2 logarithm and scaled as shown in the scale bar on the top right of the figure. All labels of groups are in Table 1 and Table S1. Assignations of ARGs to antibiotics referred to WTO ATC code J01. (c) Heatmap of significantly different relative abundance of acquired ARGs (represented by log2 RPKM in each gene) in two types of hosts, namely, human and food animals, calculated using the Wilcoxon tank-sum test with false-discovery rate (FDR) corrections. Names of ARGs are adapted from the ResFinder database. (d) Principal coordinate analyses of the relative abundance of acquired ARGs for each pair of hosts of human and food animals in the same region. Since most pigs are imported from China in Hong Kong, human in Hong Kong and China and swine from China were plotted in the same faceted panel. Each colored point or shape represents one sample with shapes and colors to differentiate hosts.