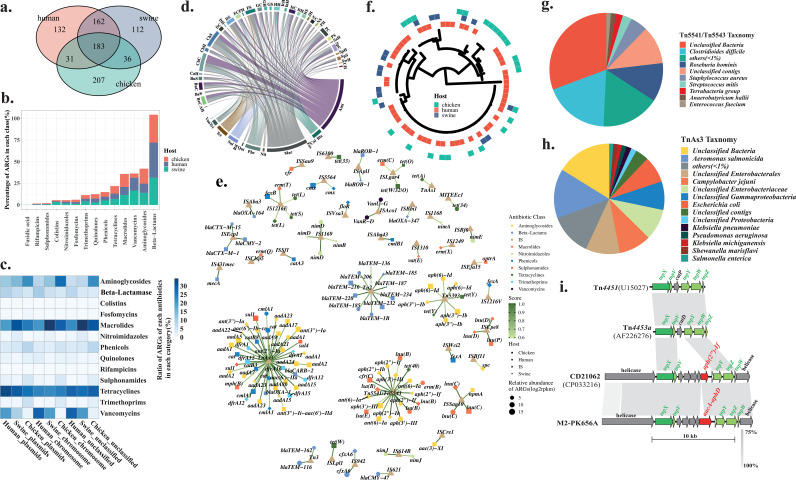
FIG 3.
Shared ARGs in humans and food animals. (a) The Venn plot of the numbers of ARGs shared by human and food animals in total. (b) Frequency of ARGs assigned to each antibiotic class in both types of hosts. (c) Heatmap of the frequencies of ARGs assigned to each antibiotic class predicted to occur in plasmids and the chromosome in both types of hosts. (d) Circos diagram shows the presence of the shared antibiotic classes conferred by ARGs associated with mobile genetic elements in both food animals and human hosts (183 ARGs). Links represent the frequencies of ARGs observed in each type of samples. Abbreviations for each type of samples can be found in Table S1; antibiotics classes and their abbreviations are as follows: vancomycin, Van; trimethoprim, Tri; tetracycline, Tet; sulfonamide, Sul; rifampicin, Rif; quinolone, Qui; phinecol, Phe; nitroimidazole, Nit; macrolide, Mac; fosfomycin, Fos; colistin, Col; beta-lactams, Bla; and aminoglycoside, Ami. (e) Network of representative ARGs shared by both types of hosts and their associated insertion sequences. The size of each shape represents the relative abundance of ARGs. The color of each shape indicates the class of antibiotic to which ARGs are resistant. The edges connected by nodes are scores that strand for the ratio of each ARGs within all ARGs associated with the same IS. (f) Phylogenetic trees of representative ARG, ant(6)-Ia, that is associated with the same IS, Tn4451/Tn4453, in both types of hosts, namely, human (red) and food animal (chicken [green] and swine [blue]). Taxonomies of contigs possessing two major groups of ISs, namely, Tn4451/Tn4453 (g) and TnAs3 (h) that are associated with ARGs. (i) The alignment of the representative Tn4451/Tn4453-like transposons (CD21062 and one human sample, namely, M2-PK656A from Hong Kong) with typical Tn4451/Tn4453.