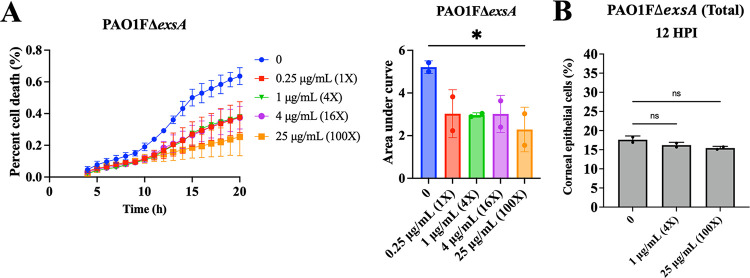
FIG 8.
Vacuolar P. aeruginosa contributes to host cell death. Quantification of corneal epithelial cell death quantified using the ratio of propidium iodide (PI)/Hoechst, also shown as the area under the curve (AUC) after internalization of P. aeruginosa PAO1FΔexsA (A) from 4 to 20 h postinfection. Extracellular bacteria were killed after 3 h with non-cell-permeable amikacin (200 μg/mL), and ofloxacin was added at 3 h (0.25 to 25 μg/mL = 1 to 100 × MIC) with continued amikacin. Intracellular survival of bacteria is shown as the percentage of corneal epithelial cells containing a GFP-expressing bacterium (pGFParabinose) treated with 0 (no ofloxacin), 1 μg/mL (4× MIC), or 25 μg/mL (100× MIC) at 12 h postinfection (B). The data show that ofloxacin-sensitive and ofloxacin-tolerant vacuolar bacteria both contribute to host cell death. *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test versus untreated control).