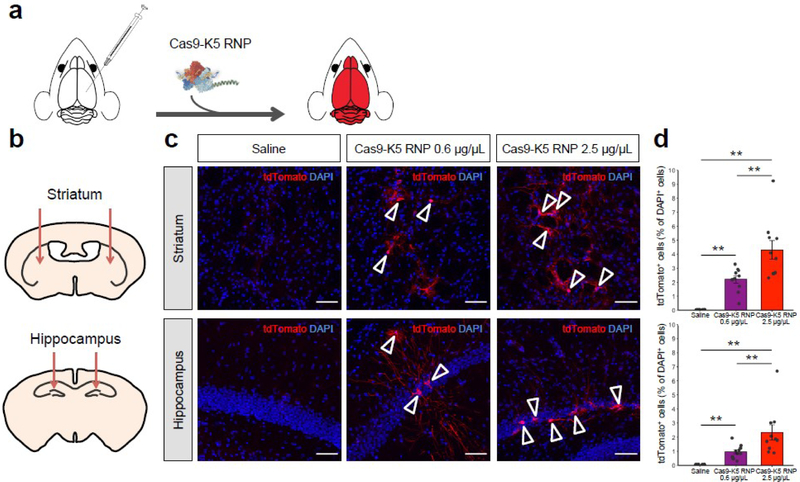
Figure 5. The Cas9-K5 RNP can edit the brains of Ai9 mice after an intracranial injection.
(a) Cas9 is fused to K5 and injected into the brains of Ai9 mice, and was able to edit neurons and astrocytes in the brain after an intracranial injection. (b) Schematic showing the injection site for the Cas9-K5 RNP, in either the striatum or hippocampus of adult Ai9 mice. Saline or Cas9-K5 RNP (0.6 μg/μL or 2.5 μg/μL) was injected into the striatum (AP: 0.50 mm, ML: ±1.87 mm, DV: −3.47 mm) or the hippocampus (AP: −2.56 mm, ML: ±1.55 mm, DV: −2.00 mm) of Ai9 mice. (c) tdTomato (red) immunostaining and DAPI (blue) nucelear staining were performed 21 days after the saline or Cas9-K5 RNP (0.6 μg/μL or 2.5 μg/μL) injection. Scale bar represents 50 μm. (d) Quantification of the percentage of tdTomato+ cells among DAPI+ cells in the striatum (permutation one-way ANOVA: F(2,27) = 27.03, P < 0.001) and hippocampus (permutation one-way ANOVA: F(2,27) = 12.93, P < 0.001). Mean ± SEM, n = 10, ** P < 0.01 by post hoc permutation t-test. Post hoc P values were calculated between control (saline) and Cas9-K5 RNP 0.6 μg/μL and 2.5 μg/μL, respectively, or Cas9-K5 RNP 0.6 μg/μL and Cas9-K5 RNP 2.5 μg/μL.