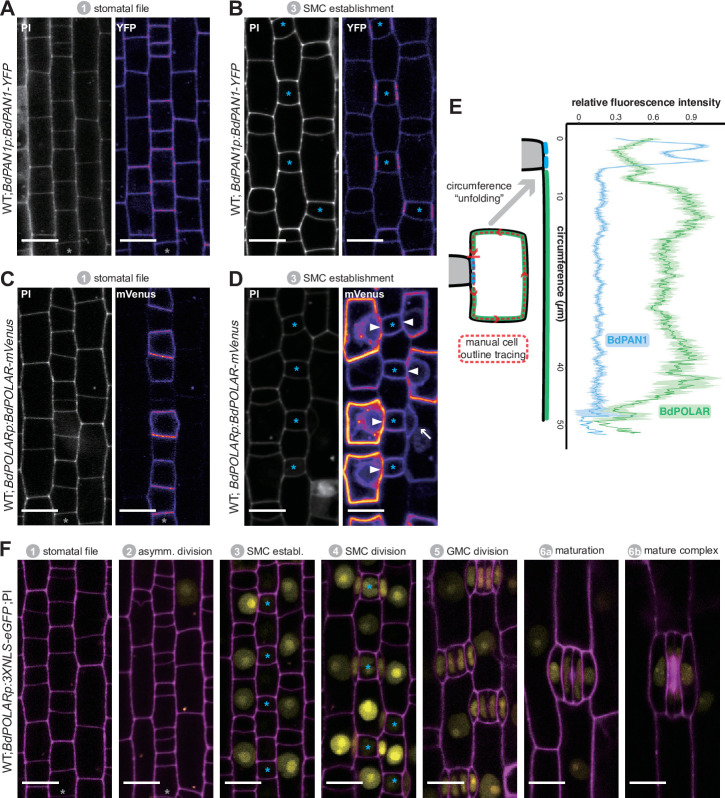
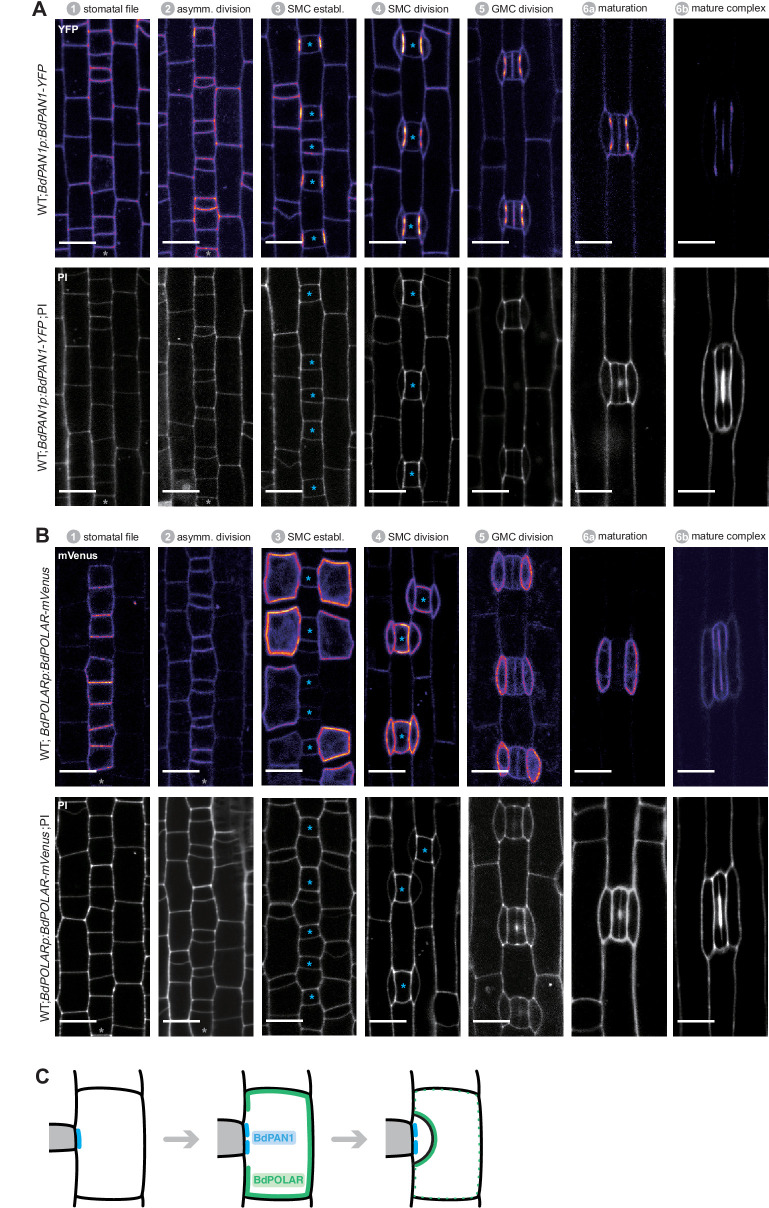
Figure 2. BdPAN1 and BdPOLAR display opposite, reciprocal polarisation in subsidiary mother cells (SMCs).
(A, B) BdPAN1p:BdPAN1-YFP reporter expression in stage 1 stomatal files (A) and during SMC stage 3 (B). Images of propidium iodide (PI)-stained cell outlines (left), and fluorescence intensity of YFP channel (right) (C, D). BdPOLARp:BdPOLAR-mVenus reporter expression in stage 1 stomatal files (C) and during SMC stage 3 (D). Images of PI-stained cell outlines (left), and fluorescence intensity of mVenus channel (right). The absence of BdPOLAR at the guard mother cell (GMC)/SMC interface is indicated with white arrowheads. The single white arrow indicates a newly formed subsidiary cell; note that BdPOLAR-mVenus dissociated from the SMC distal polarity domain. (E) Manually traced, normalised fluorescence intensity at the SMC plasma membrane of BdPAN1-YFP lines (n=13) and BdPOLAR-mVenus lines (n=8). Average fluorescence intensity with standard error is plotted as a function of the ‘unfolded’ SMC starting with the GMC/SMC interface as indicated by the model. Note that the signal gets noisy towards the end as SMCs are differently sized. Only SMCs with a length/width ratio (LWR) >0.8 for BdPAN1-YFP and LWR >0.9 for BdPOLAR-mVenus were included. (F) BdPOLARp:3xNLS-eGFP reporter expression during stomatal development. Overlay images show BdPOLAR transcriptional signals (in yellow) and PI-stained cell outlines in magenta. The stomatal files are indicated with a grey asterisk. GMCs are indicated with blue asterisks. Developmental stages are indicated. Confocal images shown are single focal planes midway from top to bottom. Scale bar, 10 µm.