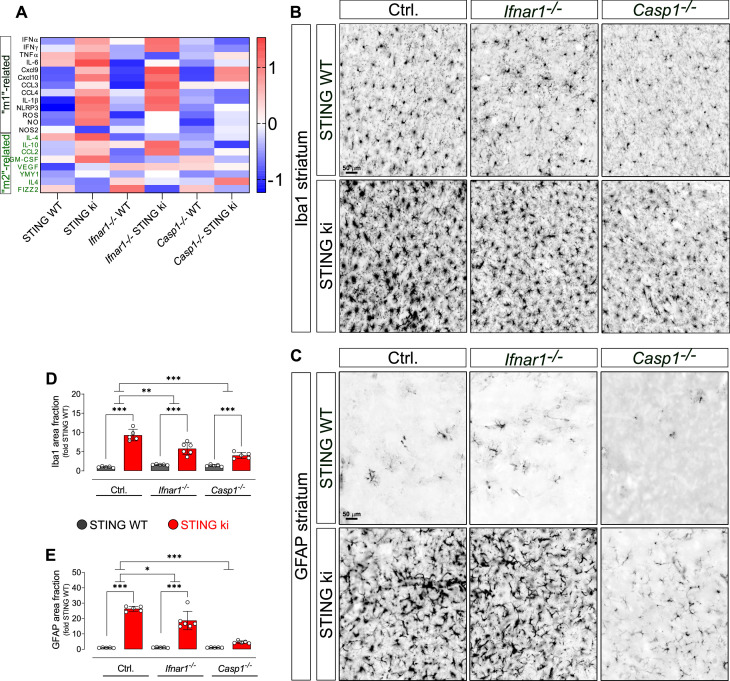
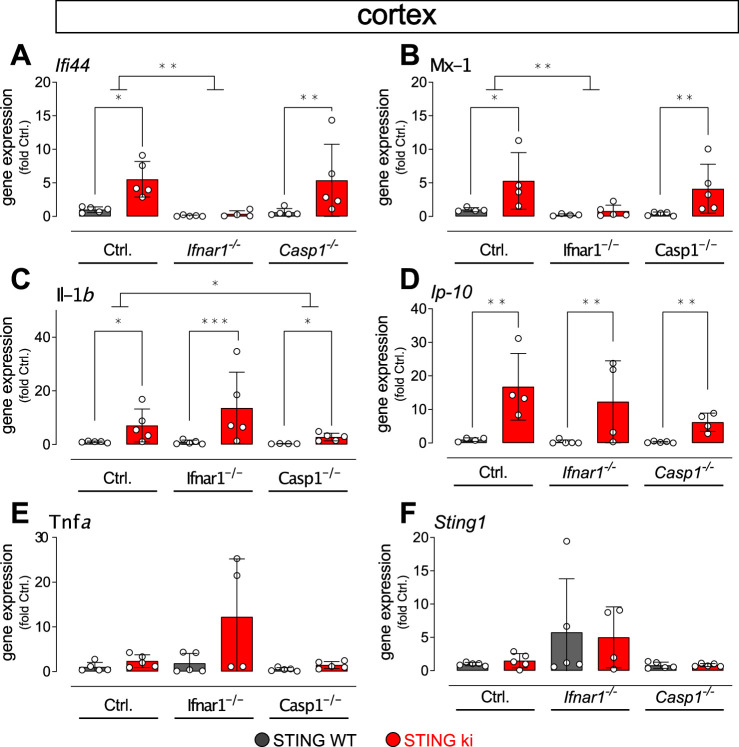
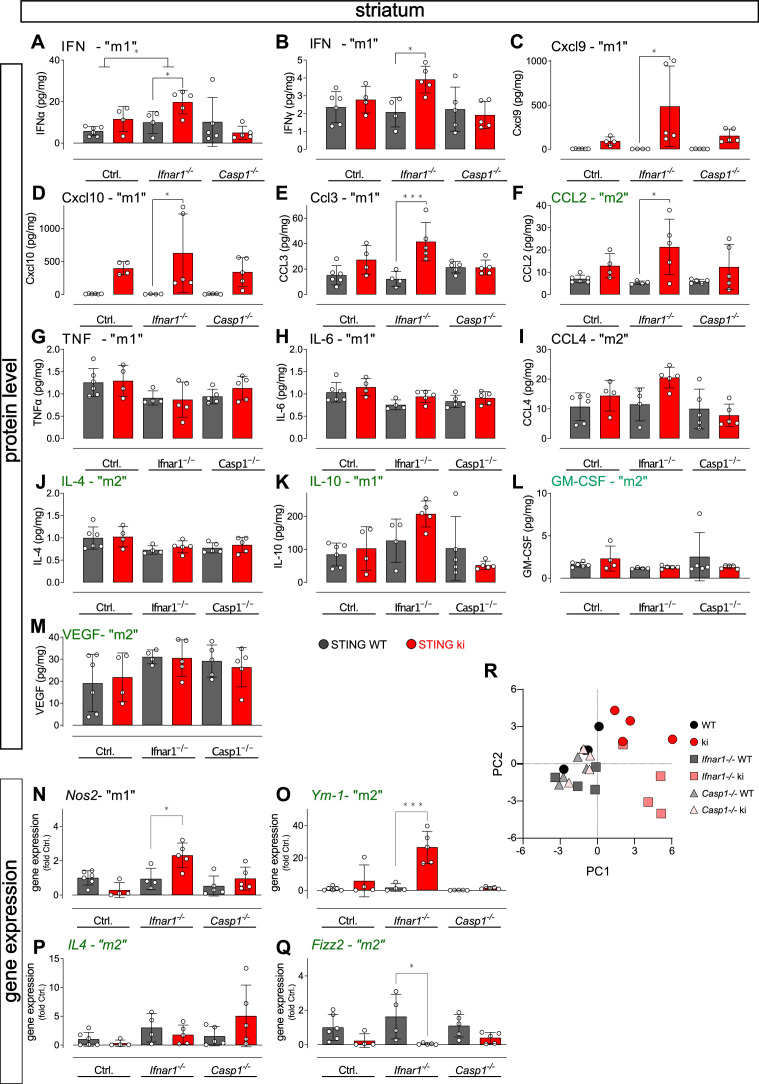
Figure 7. Neuroinflammation in adult double transgenic mice with STING ki and knock-out for Ifnar1 or Caspase-1.
(A) Heatmap showing z-scores of different inflammatory markers in double transgenic mice with STING N153S/WT ki and knock-out for Ifnar1 or Caspase-1. Graphs with data for each mediator individually are on (Figure 7—figure supplement 2). (B) Representative images of striatal sections stained for the microglia marker Iba1. Sections were obtained from adult STING WT (upper images) or STING ki (lower images) mice on a background of interferon a receptor knockout (Ifnar1-/-), caspase-1 knockout (Casp1-/-) or Ifnar1+/+, Casp1+/+ (Ctrl.). Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) Representative images of striatal sections stained for the astroglia marker GFAP from STING WT (upper images) or STING ki (lower images) mice on a background of interferon a receptor knockout (Ifnar1-/-), caspase-1 knockout (Casp1-/-) or Ifnar1+/+, Casp1+/+ (Ctrl.). Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Area fraction positive for Iba1, normalized to the mean of STING WT brains (differences in +/+ mice ***: p=0.0000001; for Ifnar1-/- ***: p=0.000003; for Casp1-/- ***: p=0.0029374; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test, n=5–6). (E) Area fraction positive for GFAP, normalized to STING WT on Ctrl. Background (***: p=0.0000 for STING WT vs STING ki on Ctrl.; ***: p=0.0000 on Ifnar1-/-; background, ***: p=0.0006 on Casp1-/- background; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test, n=5–6).