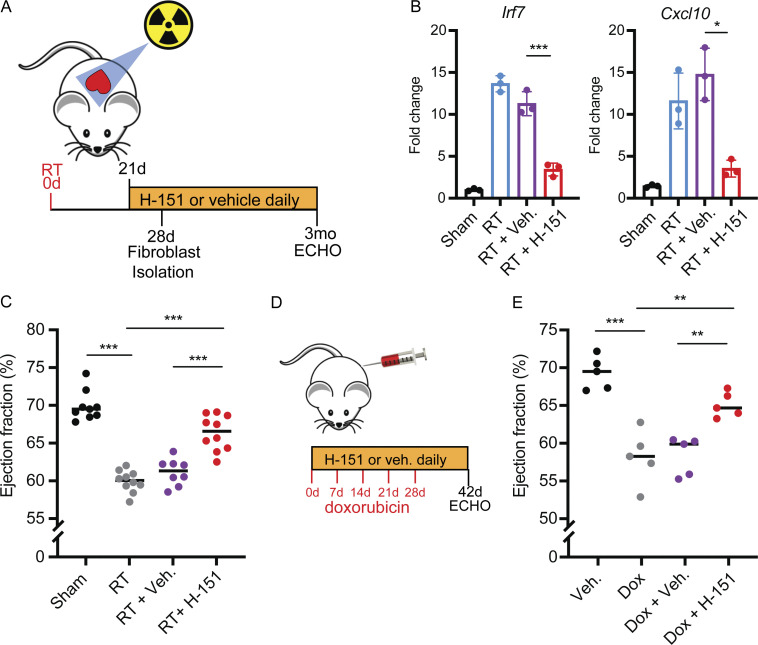
Figure 6.
A covalent STING inhibitor effectively prevents cardiac toxicity from RT and anthracyclines. (A) Schematic representation of experimental design for STING antagonist H-151 treatments following cardiac RT relative to study endpoints, echocardiogram (ECHO). (B) Irf7 and Cxcl10 gene expression in cardiac fibroblasts isolated from Sting+/+ after cardiac RT or sham treatment and subsequent treatment with H-151 or vehicle, measured by qRT-PCR; N = 3 mice for each condition; three independent experiments were performed. (C) LVEF as measured by echocardiography in Sting+/+ mice 3 mo after cardiac RT or shame treatment and subsequent treatment with either STING antagonist H-151 or vehicle until the time of echocardiography; N = 8–10 mice per condition. (D) Schematic representation of experimental design for STING antagonist H-151 treatments in mice treated with doxorubicin to induce cardiac toxicity. (E) LVEF of Sting+/+ mice 14 d after completing 5 wk doses of doxorubicin or vehicle and concurrent H-151 of vehicle until the time of echocardiography; N = 5 mice per condition. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0001, two-tailed T test.