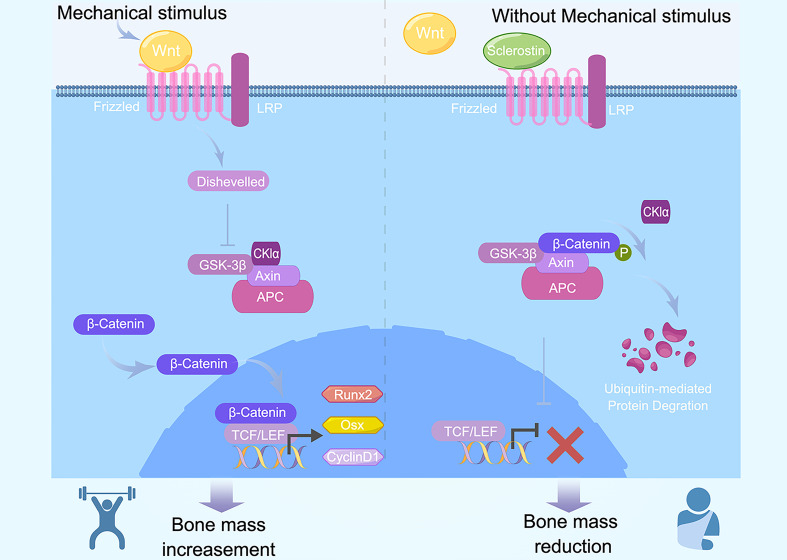
Figure 2.
Canonical Wnt signaling and sclerostin in mechanical regulation of exercise. Exercises produce mechanical stimulus and increase Wnt1. Wnt1 binds with LRP5/6, subsequently activate intercellular Dvl, resulting in release of free β-catenin and translocation into nuclei. β-cateniin binds with TEF/LEF, contributes to induction and activation of Runx2, Osx, and cyclinD1. Osteoblast differentiation and bone mass increase is activated by Wnt and inhibited by the Wnt antagonists Frizzled and sclerostin. When without mechanical stimulus bring by exercise, Wnt1 decreased and β-catenin is ubiquitinated and degraded, inducing downregulation in the expression of downstream target gene, bone mass subsequently decreased.