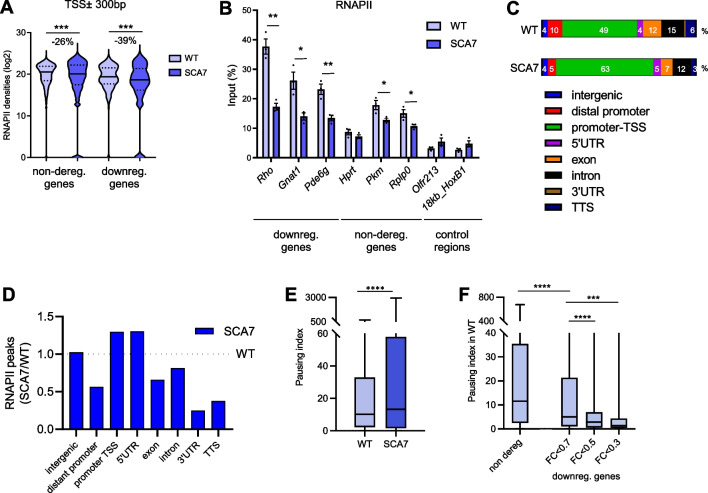
Fig. 3.
SCA7 downregulated genes have low RNAPII pausing. A Violin plots showing the decrease of RNAPII densities on TSS ± 300 bp regions of non-deregulated and downregulated genes in SCA7 retina, compared to WT. B ChIP-qPCR analysis showing the decrease of RNAPII occupancies (% of the input) on the TSS region of representative downregulated and non-deregulated genes in SCA7 retina compared to WT. Silent regions are used as controls. C Comparison of genomic distribution of RNAPII peaks in WT and SCA7 retina. Data are displayed as percentage of peaks annotated to each region relative to total number of peaks. Distant promoter (− 20 kb to − 1 kb relative to the TSS), promoter-TSS (− 1 kb to + 100 bp at the TSS), and TTS (− 100 bp to + 1 kb relative to the TTS). D Graph representing the ratio of RNAPII peak distribution in different genic and intergenic regions in SCA7 and WT retina. E Graph showing the comparison of RNAPII pausing index in WT and SCA7 retina for all expressed protein coding genes. F Graph showing the comparison of RNAPII pausing index at basal level in WT retina for non-deregulated gene sets and SCA7 downregulated genes with different fold change (FC). Data in A, E and F were analyzed using Mann–Whitney test. Data in B are normalized as percentage of input DNA signal, expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3 mice/genotype) and analyzed using two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001