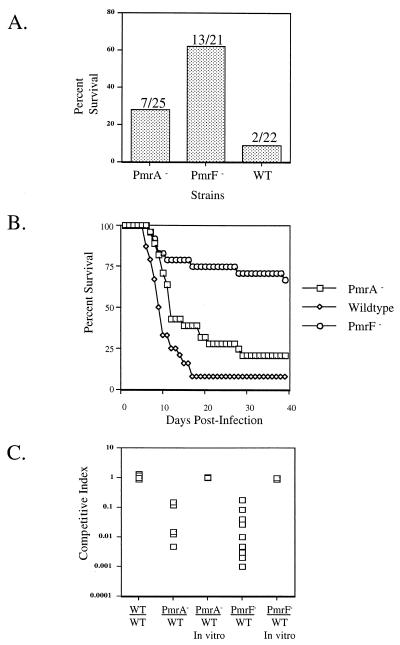
FIG. 8.
Mutations in pmrA or the pmrHFIJKLM operon affect virulence by the oral route. Mice were inoculated orally with a dose of 106 CFU. BALB/c mice were infected with ATCC 14028s (WT), WT with a pmrA::Tn10d insertion (PmrA−), WT with a pmrF::Tn10d insertion (PmrF−), or a combination of two of these strains. (A) Percent survival of BALB/c mice receiving the WT, PmrA−, or PmrF− strain. The numbers above the bars represent the number of surviving mice per the number of mice tested. (B) Percent survival of mice over 40 days postinfection. (C) Competition assays of WT versus PmrA− and WT versus PmrF− strains. The competitive index is the ratio of CFU in the livers of mice infected with a PmrA−, WT, or PmrF− strain to CFU in livers of mice infected with the WT strain. The WT-versus-WT experiment involved two WT strains marked with different antibiotic resistances. The competitions labeled in vitro were performed by growth overnight in LB medium to ensure that any in vivo effects were not due to a growth disadvantage. Both liver and spleen were examined in the competition assays, but only the data for the liver are shown.