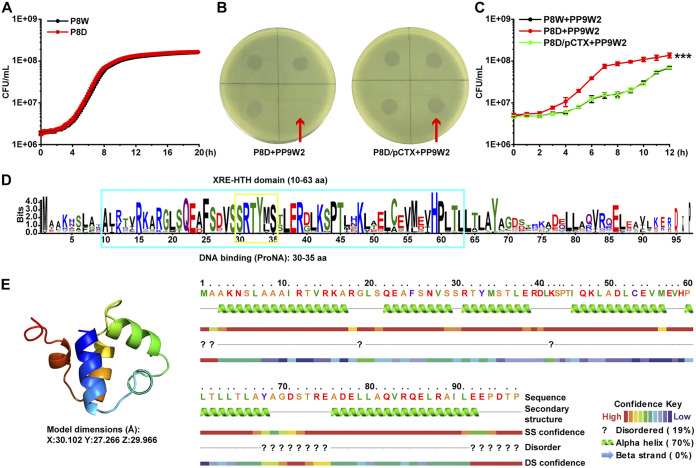
FIG 1.
A hypothetical XRE-type transcriptional regulator, LfsT, impacts the sensitivity of bacterial strain P8W to phage PP9W2. (A) Growth experiment in LB medium for 12 h. The differently colored lines represent P8W and P8D (ΔlfsT). (B) Complementation (plasmid pCTX carrying the lfsT gene) restored host phage sensitivity in a spotting assay. (C) Growth inhibition of PP9W2 on the indicated strains (LB medium supplemented with 100 mg/L ampicillin) at an MOI (multiplicity of infection) of 1. The differently colored lines represent P8W, P8D, and P8D/pCTX. (D) Protein domain prediction for LfsT. The blue box represents an XRE-HTH domain from aa 10 to 63. The yellow box represents a DNA binding site from aa 30 to 35. More highly conserved amino acid residues are indicated by larger letters. (E, left) Protein structural model of LfsT built using SWISS-MODEL. The image is rainbow colored from the N to the C termini. (Right) Protein secondary structure of LfsT. The experiments were independently replicated three times, and each sample was tested in triplicate (A to C). Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (α < 0.05) to examine the mean differences between the data groups. ***, P < 0.001. Error bars show standard deviations. SS, secondary structure; DS, disorder structure.