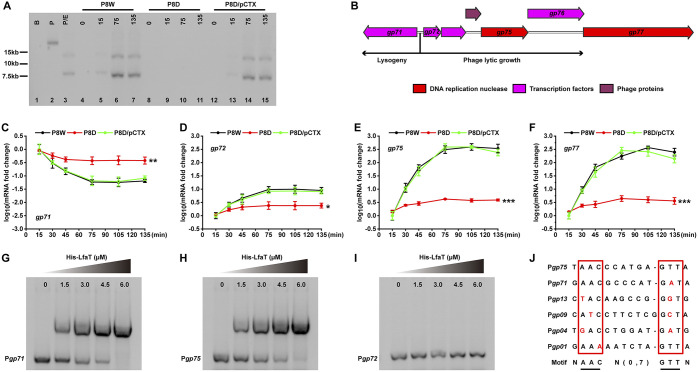
FIG 2.
LfsT binds directly to the promoters of the gp71 gene and other crucial phage genes to influence phage replication. (A) Southern blotting (detailed in Materials and Methods). The genomic DNA in all lanes was digested with FseI, except for lane 2. Lane 1 (B), P8W genomic DNA; lanes 2 and 3 (P and P/E), phage PP9W2 genomic DNA; lanes 4 to 15, total DNA of different bacterial cells infected with phage PP9W2 at the indicated time intervals (0, 15, 75, and 135 min); lanes 4 to 7, P8W cells; lanes 8 to 11, P8D cells; lanes 12 to 15, P8D/pCTX cells. (B) Information on genes flanking the gp71/gp72 switch. The differently colored squares represent various proteins as indicated above. (C to F) RT-qPCR assay of the genes using cDNA of different strains infected with phage PP9W2 at the indicated time intervals. gp71 encodes a CI-like repressor protein, gp72 encodes a Cro-like repressor protein, gp75 encodes the putative helicase DnaK, and gp77 encodes the putative helicase DnaB. (G to I) EMSAs of different promoter fragments using the purified His-tagged LfsT protein. (G and H) LfsT binding to the gp71 or gp75 promoter; (I) Negative control. The purity of the His-tagged LfsT protein is about 97.9%. (J) Predicted LfsT binding sites of different promoters. gp13 encodes the putative tail component, gp09 encodes the phage gp6-like head-tail connector protein, gp04 encodes the phage portal protein, and gp01 encodes the terminase small subunit. A partial palindromic motif was speculated to be AACN(0,7)GTT. Red letters represent probable mutation sites. Each sample was tested in triplicate, and the experiments were independently replicated three times (C to F). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (α < 0.05) to examine the mean differences between the endpoints of data groups. Error bars show standard deviations. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.