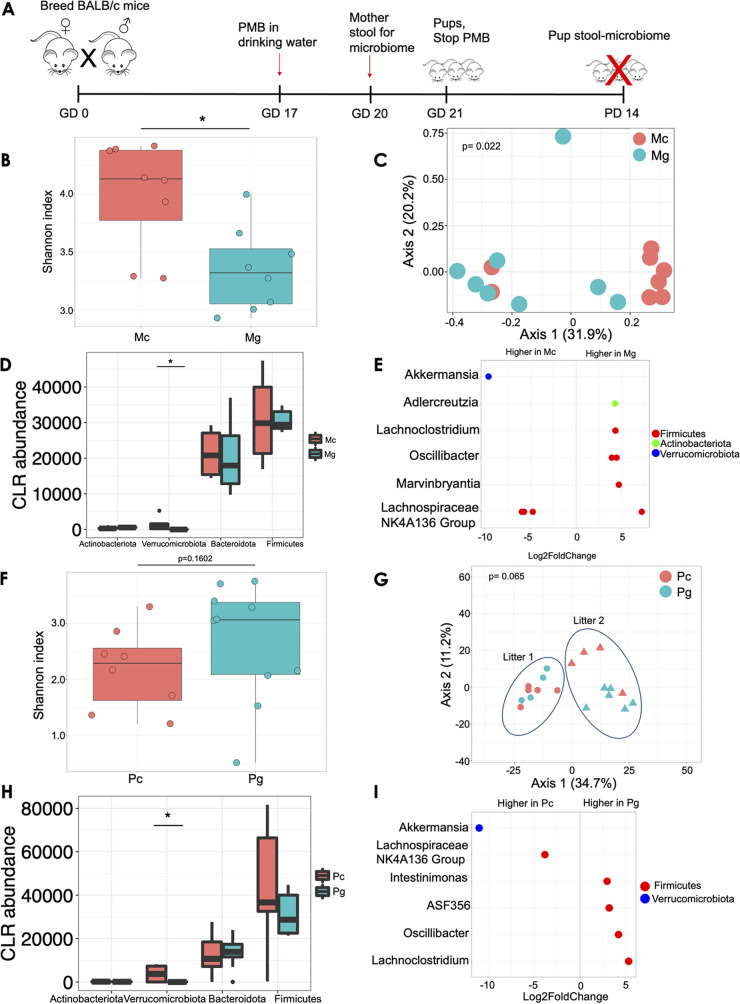
FIG 1.
Oral antibiotics prior to delivery induce shifts in maternal and offspring gut communities. (A) Experimental design. Pregnant BALB/c dams were treated with polymyxin B in drinking water (1 mg/mL) starting at gestational day (GD) 17 until delivery, when antibiotic treatment was stopped. At gestational day 20, maternal stools were collected for 16S marker gene analysis. Pup gut microbiota was assessed at postnatal day (PD) 14. (B) Shannon alpha diversity between dams that received polymyxin B (Mg) versus control dams (Mc). (C) PCoA of maternal microbiota during pregnancy determined by the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity metric. (D) CLR abundance of bacteria in pregnant dams at the phylum level. (E) Differentially abundant genera by DeSEq2 during pregnancy. (F) Shannon alpha diversity of stool microbiota in pups born to polymyxin B-treated dams (Pg) and control pups (Pc). (G) PCoA of pup fecal microbiota determined by Bray-Curtis dissimilarity. (H) CLR abundance of pup microbiota at the phylum level. (I) Differentially abundant genera determined using DeSEq2 in pups. Pup microbiota were analyzed from two dams per group (two litters). Pregnant dams were separated and housed in individual cages prior to delivery. Data are representative of two independent experiments. N = 8 per group for dams and 9 to 10 per group for pups. *, P < 0.05.