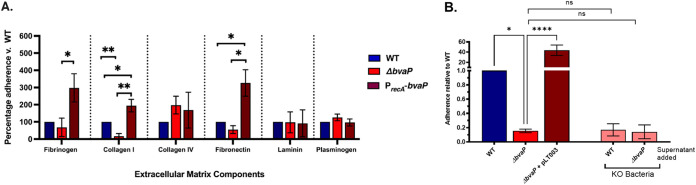
FIG 6.
BvaP is necessary for proficient binding to some ECM components and human vaginal epithelial cells in vitro. (A) Adherence assays using the extracellular matrix components human fibrinogen, collagens I and IV, fibronectin, and laminin using the WT, the ΔbvaP strain, and the overexpression construct ΔbvaP/pLT003. (B) Adherence assays using human vaginal epithelial cells (VK2) at an MOI of ~10 show decreased binding of the bvaP mutant strain and increased binding of the strain overexpressing bvaP. Pink bars, ΔbvaP cells incubated with the WT or ΔbvaP supernatant prior to adherence. The addition of the WT supernatant did not result in increased binding of the ΔbvaP strain to VK2 cells. Assays were completed in at least technical triplicate for each data point. Averages from ≥3 biological replicates ± standard errors of the means (SEM) are shown. Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Kruskal-Wallis post hoc test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant). KO, knockout.