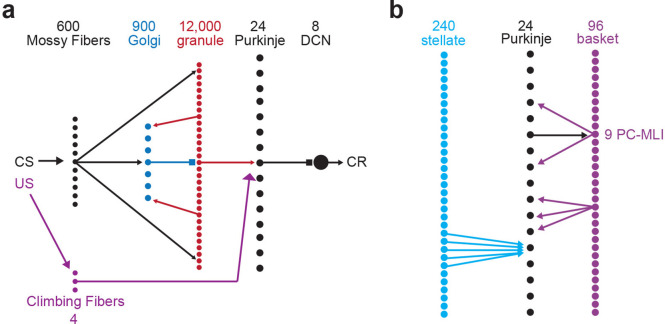
Figure 14. Schematic representation of connectivity in the cerebellar simulation.
(a) Indicates two inputs to the cerebellum -- mossy and climbing fibers -- and a schematic representation of the connectivity of four cerebellar neuron types. The number of each cell type represented in the simulation are indicted by numbers at top. Mossy fiber inputs diverge to excite Golgi and granule cells and converge to excite deep cerebellar neurons (DCN); the latter is not shown on the diagram. Granule cells excite Purkinje and Golgi cells, while Golgi cells inhibit nearby granule cells. (b) Schematic representation of the connectivity between molecular layer interneurons (MLIs) and Purkinje cells (PCs). Stellate cells converge to inhibit PCs. PCs inhibit a subset of basket cells near them (the PC-MLIs) and basket cells inhibit nearby PCs, excluding those that could form reciprocal connections.