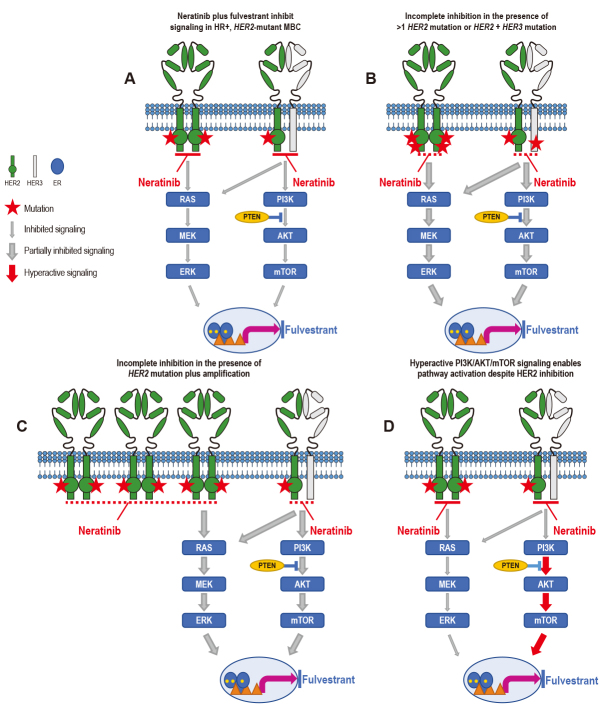
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of resistance to neratinib. (A) Neratinib plus fulvestrant inhibit signaling in HR+, HER2-mutant MBC. In patients whose tumors harbor a single somatic activating mutation (red star) in HER2, neratinib strongly inhibits (thin gray arrow) HER2 pathway signaling, whereas fulvestrant inhibits ER signaling, leading to tumor growth inhibition. (B) Neratinib is less effective against/partially inhibits signaling in (thick gray arrow) tumors with more than one HER2 mutation or HER2 mutation plus HER3 mutation or (C) HER2 mutation plus amplification, whether these dual alterations are intrinsic or acquired. (D) Hyperactivation (thick red arrow) of downstream signaling can also preclude the effect of neratinib on mutant HER2. ER: Estrogen receptor; HR: hormone receptor; MBC: metastatic breast cancer.