Figure 1.
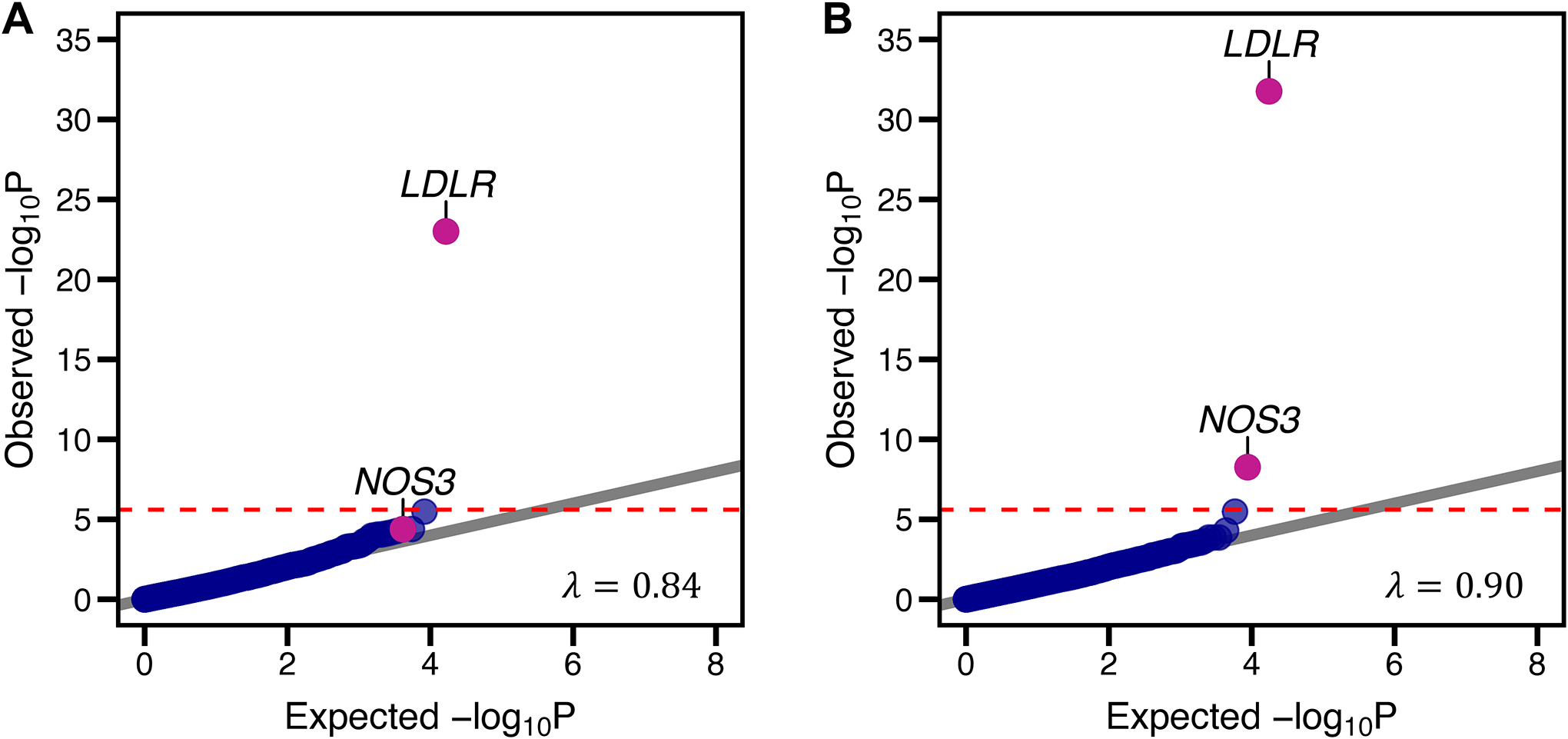
Association of predicted loss-of-function variants and risk of coronary artery disease. Rare DNA variants predicted to lead to loss-of-function, disrupt mRNA splicing, or annotated as pathogenic or likely pathogenic within the ClinVar database were aggregated within each gene (‘pLoF’ strategy). Panel A) is a quantile-quantile plot of observed versus expected p-value distributions observed using this strategy. A second variant annotation strategy (‘pLoF+missense’) additionally included ultra-rare missense variants predicted to be damaging by each of five computational prediction algorithms within each gene. Panel B) is a quantile-quantile plot of observed versus expected p-value distributions of this mask. The horizontal line represents the Bonferroni-corrected p-value threshold of 1.25 × 10−6, assuming 20,000 genes tested and two rare variant grouping masks used. λ refers to the genomic inflation factor, with values significantly higher than 1 suggestive of inadequate control for population stratification.
LDLR – low-density lipoprotein receptor; NOS3 – endothelial nitric oxide synthase (NOS3).
