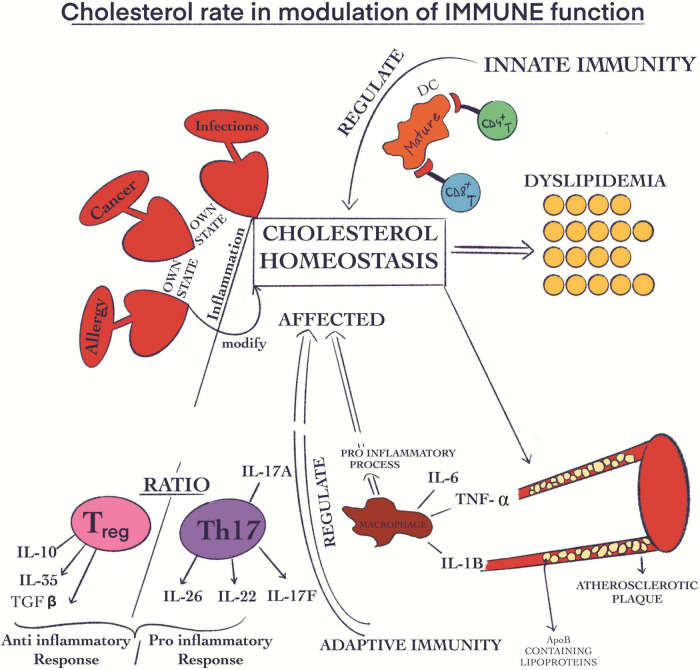
FIGURE 4.
Cholesterol rate in the modulation of immune function. Some diseases, such as cancer, infections, and allergies, are capable of modifying the cholesterol biochemical equilibrium through their own state of inflammation; Atherosclerosis and dyslipidemia are negative effects of the increased cholesterol biosynthesis; The ApoB-containing lipoproteins are accumulated in endothelial place; This phenomenon has pro-inflammatory effects; The inflammation is correlated with the generation of certain cytokines like (TNF) α, IL6, and (IL)1β; The Treg cells have an anti-inflammatory effect; Th17 cells are involved in the pro-inflammatory process; The decline of Treg/Th17 ratio is linked with long-term inflammation.