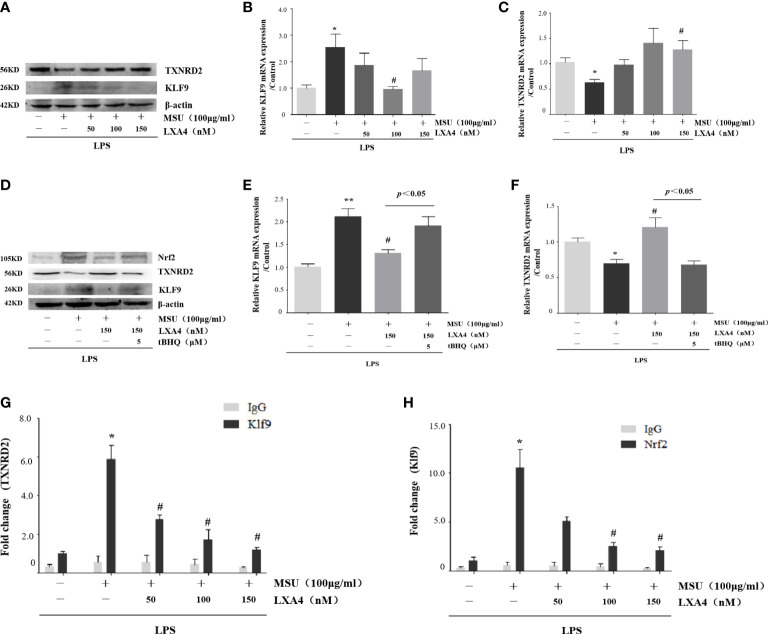
Figure 7.
LXA4 interdicts Nrf2/Klf9/TXNRD2 signaling pathway. The PMA-differentiated THP-1 macrophages were primed with LPS (300 ng/ml) for 3 h and then pretreated with LXA4 (50–150 nM) for 1 h; subsequently, 100 μg/ml of MSU crystals was added for 24 h. (A) Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting to determine the Klf9 and TXNRD2 protein levels. (B, C) RT-qPCR was performed to measure the TXNRD2 and Klf9 mRNA levels (n=5). The PMA-differentiated THP-1 macrophages were primed with LPS (300 ng/ml) for 3 h and then pretreated with LXA4 (150 nM) and tBHQ (5 μM) for 1 h; subsequently, 100 μg/ml of MSU crystals were added for 24 h. (D) Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting to determine the Nrf2, Klf9, and TXNRD2 protein levels. (E, F) RT-qPCR was performed to measure the TXNRD2 and Klf9 mRNA levels (n=4). The PMA-differentiated THP-1 macrophages were primed with LPS (300 ng/ml) for 3 h and then pretreated with LXA4 (50–150 nM) for 1 h; subsequently, 100 μg/ml of MSU crystals was added to stimulate for 24 h. (G, H) The chromatin was immunoprecipitated with control (IgG) or Nrf2- and Klf9-specific antibody, followed by the reversal of the cross-linking and DNA isolation. DNA was used in quantitative PCR with primers specific for Klf9 and TXNRD2 promoter or irrelevant GAPDH promoter (n=4). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM, * p<0.05 and ** p<0.01 compared with the vehicle group, # p<0.05 compared with the MSU group.