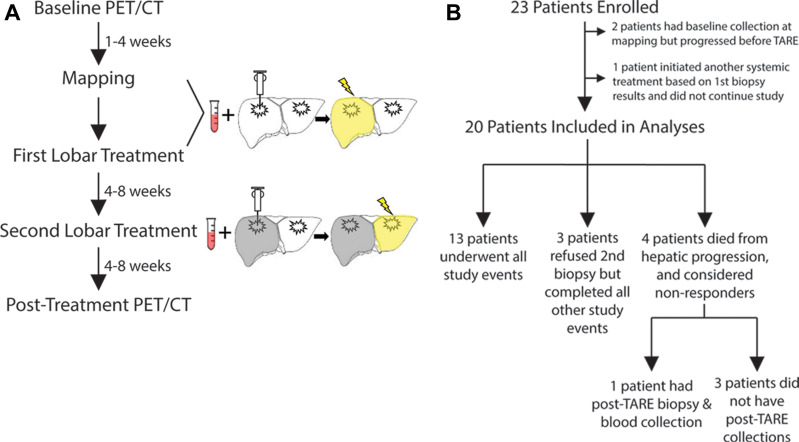
Figure 1:
Study schema. (A) Participants underwent a mapping procedure, two separate transarterial radioembolization (TARE) procedures, baseline and post-TARE blood collection and liver tumor biopsy, and PET/CT before and after TARE. (B) Of 23 participants initially enrolled, 20 were included in the study analyses. Three participants refused a second biopsy but underwent all other study events. Four participants died due to hepatic progression after the first TARE; of these, one underwent a post-TARE biopsy and blood collection during a paracentesis, while the other three had no follow-up tissue collection.