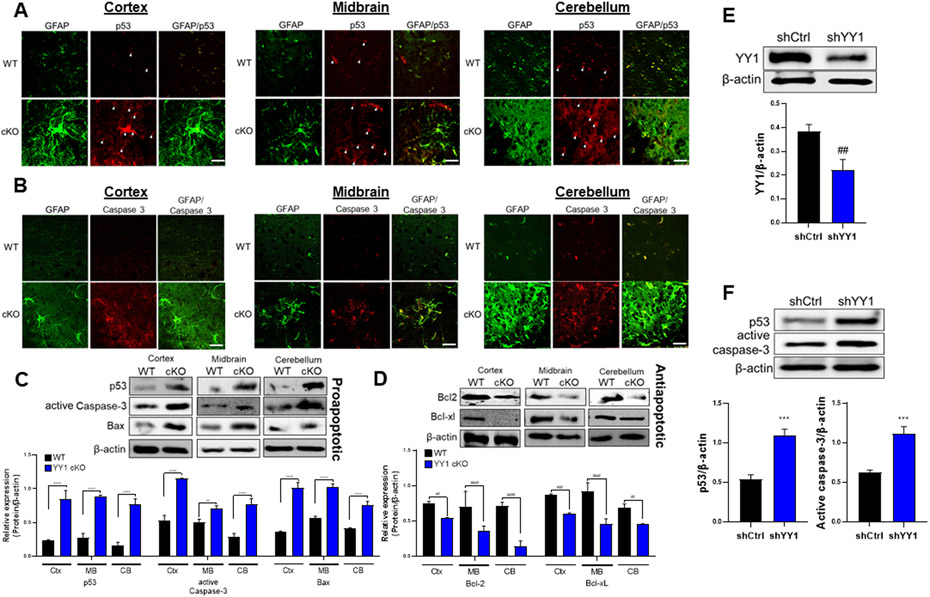
Figure 7. Deletion of astrocytic YY1 regulates brain apoptosis.
(A-B) Coronal sections of brain tissues were immunostained with GFAP and p53 or caspase-3. The expression of GFAP and p53/caspase-3 were shown as green and red fluorescence signals, respectively, in the cortex, midbrain, and cerebellum of the WT and YY1 cKO mouse brain (×40 magnification with a confocal microscope, scale represent 50 μm). (C-D) Cortex, midbrain, and cerebellum regions were processed for proapoptotic proteins (i.e., p53, active caspase-3, and Bax) (C) and antiapoptotic proteins (i.e., Bcl-2, Bcl-xL) (D) by western blotting. (E-F) Human H4 astrocytes were transduced with shRNA lentiviral particles for YY1 knockdown and control, followed by detection and quantification of the proteins YY1 (E), p53 and active caspase-3 (F). β-actin was used as a loading control for protein. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001; ##, p<0.01; ###, p<0.001; ####, p<0.0001 compared with the control (WT) (Student t-test, n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD.