Figure 5.
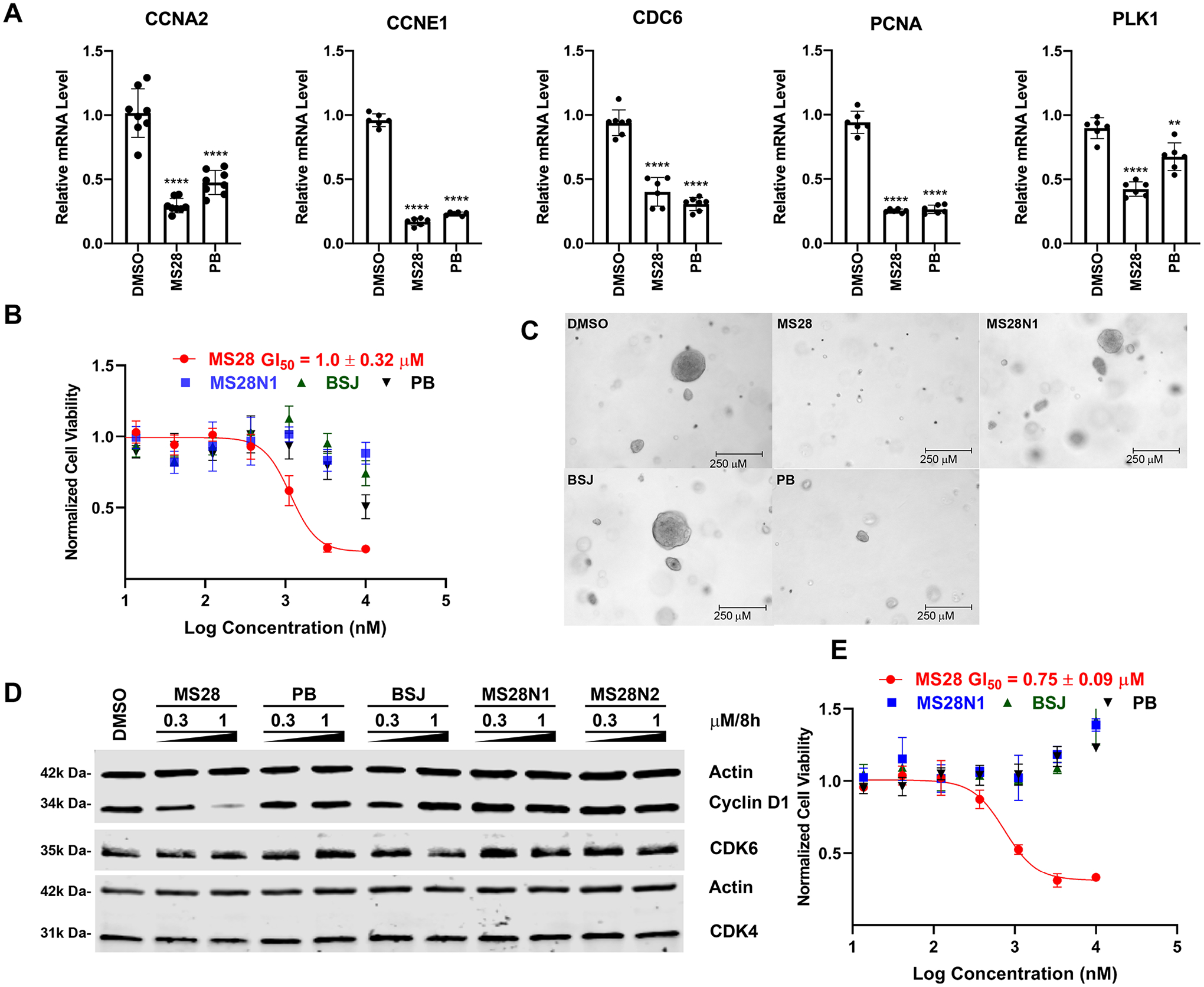
MS28 effectively suppresses the downstream Rb-E2F pathway, proliferation, and tumorigenesis in cancer cells. (A) MS28 and PB significantly reduced mRNA levels of E2F target genes (CCNA2, CCNE1, CDC6, PCNA, and PLK1) in RT-qPCR studies. Calu-1 cells were treated with DMSO, 3 μM of MS28, or PB for 8 h. P-values were calculated in comparison to DMSO from two biological repeats. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05. (B) MS28 inhibits cell growth much more effectively than PB, BSJ, and MS28N1 in Calu-1 cells (treated with the indicated compound for 5 days). Data shown are the mean values ± SD from two biological repeats (each with three technical repeats). (C) MS28 suppresses clonogenicity of Calu-1 cells in a soft agar assay more effectively than PB, BSJ, and MS28N1. Images were taken at the end of the 20-day treatment. Each treatment group (at 0.3 μM) is representative of three independent experiments, each with at least five technical repeats. (D) MS28, not MS28N1, BSJ, or PB, effectively degrades cyclin D1 in NCI-H2110 cells (treated with the indicated compound at the indicated concentrations for 8 h). Results are representative of two biological repeats. (E) MS28, but not MS28N1, BSJ or PB, potently inhibits the growth of NCI-H2110 cells (5 days treatment, three biological repeats).
