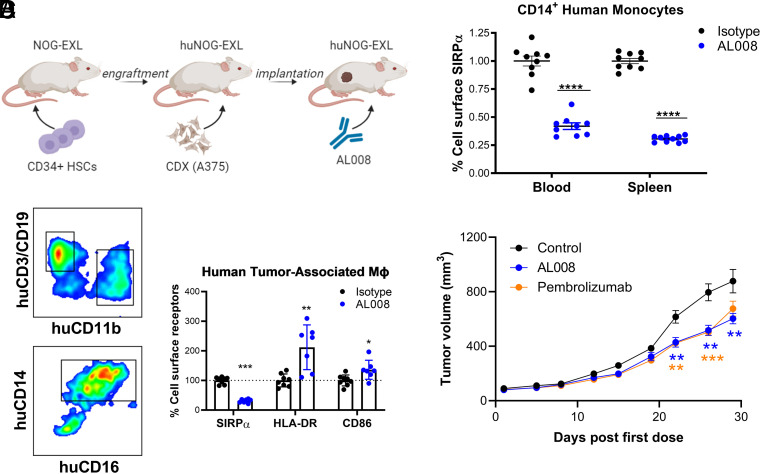
FIGURE 6.
Effect of AL008 on human tumor-associated macrophages in a humanized mouse model. (A) Immune-deficient NOG-EXL mice were engrafted with human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) for stable reconstitution of human immune cell lineages. Mice were then implanted s.c. with 3 million cells of A375. When tumors reached a volume of 200–400 mm3, mice received two doses of AL008 or isotype control 3 d apart. Twenty-four hours after the last dose, blood, spleen, and tumor tissues were harvested and processed for analysis by flow cytometry. (B) AL008 internalizes SIRPα on peripheral myeloid cells. Human monocytes from blood and spleen samples were gated on human CD45+CD11b+CD14+CD16− cells. Cell surface SIRPα was detected by flow cytometry with a fluorescent anti-human SIRPα Ab, as previously described. Relative expression levels of SIRPα were normalized to the isotype-treated animals. Each symbol represents a different animal in the group. ****p < 0.0001. (C) AL008 internalizes SIRPα and increases M1 markers on human tumor-associated macrophages. Macrophages were gated on human CD45+CD11b+CD14+CD16+ cells. A representative gating scheme is shown. Cell surface SIRPα, HLA-DR, and CD86 were detected by flow cytometry. Relative expression levels of the indicated receptor were normalized to the isotype-treated animals. Each symbol represents a different animal in the group. (D) Humanized mice implanted with MDA-MB-231 tumors were administered isotype (n = 7), AL008 (n = 8), or the anti–PD-1 Ab pembrolizumab (n = 7). AL008 inhibited tumor growth in a similar manner to pembrolizumab. In (B)–(D), unpaired Student t tests were performed. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 for treatment versus isotype murine IgG1 at a given time point.