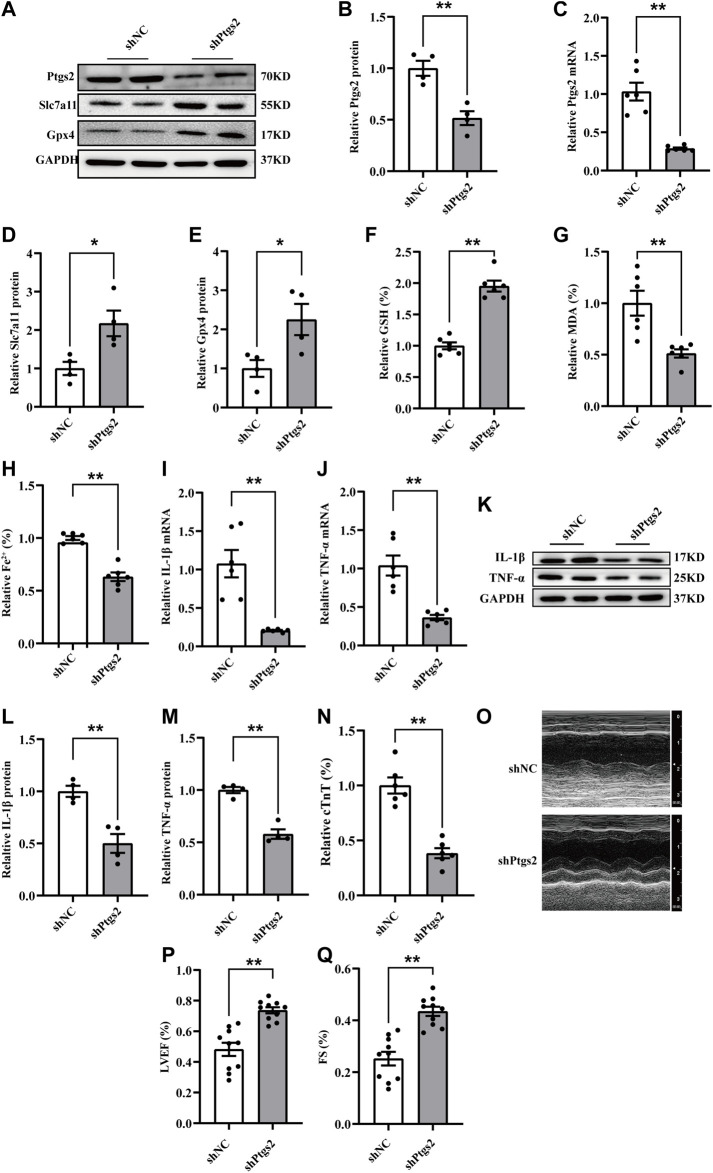
FIGURE 3.
Ptgs2 silencing ameliorated ferroptosis-mediated myocardial injury and inflammation following CME. (A–C) The efficiency of Ptgs2 silencing in mRNA (n = 6) and protein (n = 4) level. (D,E) The expression levels of Gpx4 and Slc7a11 determined by western blotting (n = 4). (F–H) Levels of GSH, Fe2+, and MDA in myocardial tissues (n = 6). (I,J) The mRNA levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in each group (n = 6). (K–M) Western blotting showing the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α (n = 4). (N) Serum levels of cTnT were decreased in the shPtgs2 group (n = 6). (O–Q) Cardiac LVEF and FS detected by echocardiography (n = 10). GAPDH served as an internal control was performed to quantitatively normalized the protein data. Data are presented as the normalized mean ± SEM (to shNC) or mean ± SEM. Values in shNCs were averaged and normalized to 1 (A–N).*p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. CME: coronary microembolization; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; FS: fractional shortening; cTnT: cardiac troponin T; Gpx4: glutathione peroxidase 4; Slc7a11: solute carrier family 7 member 11; Ptgs2: prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase-2; MDA: malondialdehyde; GSH: glutathione; IL-1β: interleukin 1 beta; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha.