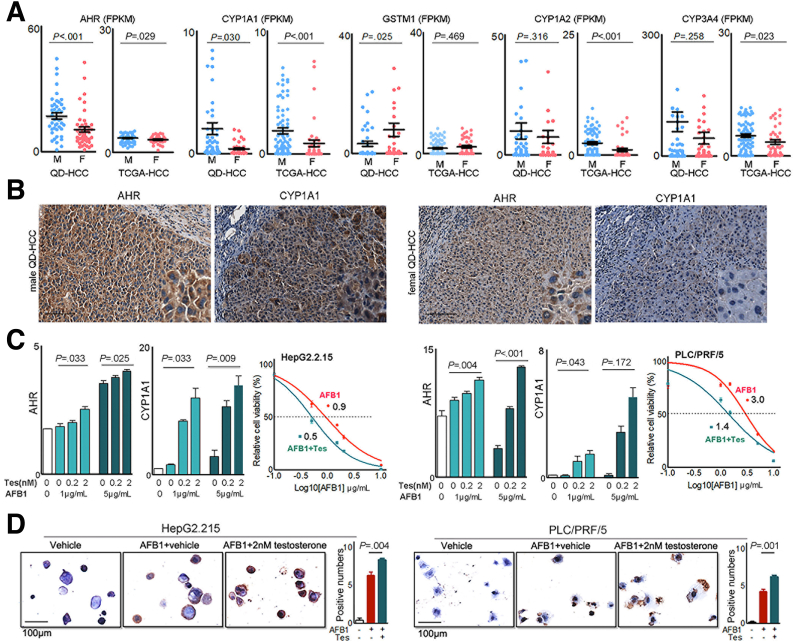
Figure 7.
Sex hormones on gene expression related to aflatoxin metabolism. (A) Expression levels of the genes in QD-HCCs and TCGA-HCCs. (B) Expression of AHR and CYP1A1 determined by immunohistochemistry in QD-HCCs. Shown are the representatives from 10 male samples and 10 female samples. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Bar graphs show AHR and CYP1A1 expression levels in HepG2.2.15 (left) and PLC/PRF/5 (right) in the presence of different concentrations of testosterone after AFB1 treatment, determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as control. The curves show AFB1 toxicity on HepG2.2.15 (left) and PLC/PRF/5 (right) in the presence of 2 nmol/L testosterone (blue lines, AFB1+Tes) or AFB1 only (red lines, AFB1). (D) Images show the AFB1–DNA adducts (brown) in HepG2.2.15 (left) and PLC/PRF/5 (right) detected by immunohistochemistry, after AFB1 treatment only (AFB1+vehicle) or in the presence of 2 nmol/L testosterone (AFB1+Tes). Bar graphs indicate the average AFB1–DNA positive numbers every 10 cells in 5 fields of 3 independent experiments. F, female; FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million fragments mapped; M, male.