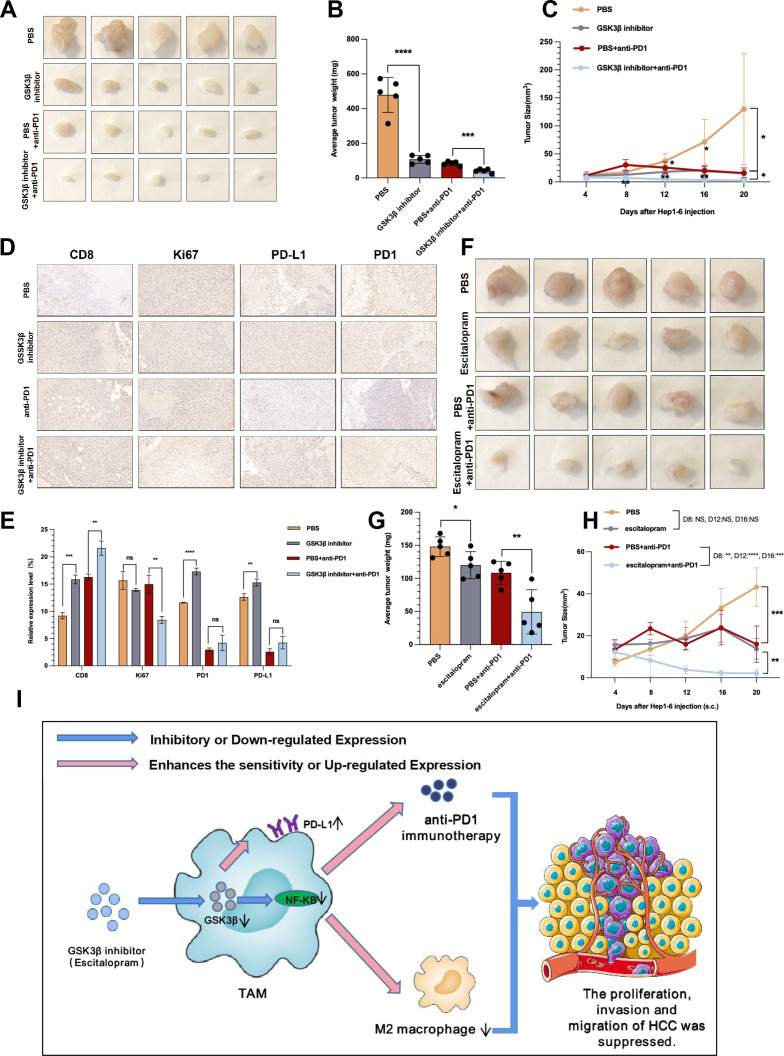
Figure 7.
Escitalopram reduced tumor growth in mice and increased the efficacy of anti-PD1 treatment against HCC. (A) Images of subcutaneous tumors in each group (PBS, GSK3β inhibitor, anti-PD1, GSK3β inhibitor+ anti-PD1). (B, C) Analysis of subcutaneous tumors in the respective groups. (D, E) Immunohistochemistry results of CD8, Ki67, PD-L1 and PD1 expression in the respective groups. (F) Images of subcutaneous tumors in each group (PBS, escitalopram, anti-PD1, and escitalopram+anti-PD1). (G, H) Analysis of subcutaneous tumors in the respective groups. (I) Pattern diagram showing that macrophage GSK3β deficiency inhibits the development of HCC and enhances the sensitivity of anti-PD1 immunotherapy. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. ****p<0.0001. ns indicated no significant different. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage.