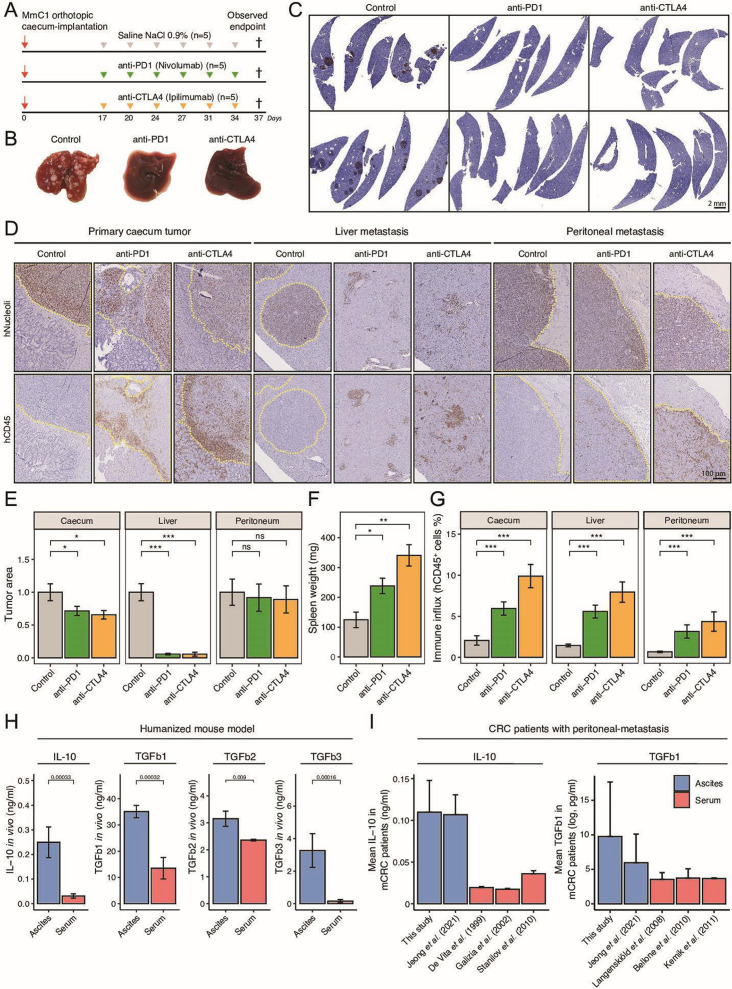
Figure 3.
Eradication of liver metastasis but not peritoneal metastasis by ICB therapy. (A) Experimental protocol of treating HIS mice with anti-PD-1 (200 µg, i.p.) or anti-CTLA-4 (200 µg, i.p.), starting post 17 days orthotropic cecum-implantation. N=5 mice per group. All animals are sacrificed at the first observed endpoint of control mice. (B) Example livers of control, anti-PD-1-treated and anti-CTLA-4-treated mice at observed endpoint of control group. (C) Histological hNucleoli staining examples of liver sections from two different mice per group. Scale-bar is 2 mm (D) Histological hNucleoli (top) and hCD45 (bottom) staining of primary cecum tumor, liver metastasis, and peritoneum metastasis. Dashed yellow line indicates tumor/metastasis area. Scale-bar 100 µm. (E) Tumor/metastasis area (hNucleoli mm2 in cecum, liver, and peritoneum. (F) Splenic weight (mg) at observed endpoint of control group, representative for degree of splenomegaly. (G) Total immune infiltration (hCD45% relative to tissue) in cecum, liver, and peritoneum. (H) Immune suppressive cytokine levels of IL-10, TGFb1, TGFb2 and TGFb3 in ascites versus serum samples of HIS mice. (I) Mean IL-10 and TGFb1 concentration in ascites or serum samples of human patients with metastatic CRC.43–49 Data shown as mean±SEM. Mann-Whitney: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001; CRC, colorectal cancer; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocytes-associated protein 4; HIS, human immune system; ICB, immune checkpoint blockade; IL, interleukin; i.p., intraperitoneal injection; mCRC, metastatic CRC; ns, not significant; PD-1, programmed death ligand-1; TGF, transforming growth factor.